謎題生成演算法:從回溯法到約束滿足問題
深入了解謎題生成的技術原理
🎯 引言:謎題生成的挑戰
謎題生成是一個迷人的演算法挑戰,它結合了數學、邏輯和計算機科學的多個領域。無論是經典的數獨、迷宮,還是現代的單詞搜尋遊戲,每個謎題背後都有精心設計的生成演算法。
💡 謎題生成的核心挑戰
- 解的存在性:確保生成的謎題至少有一個解
- 唯一解性:保證謎題只有一個唯一解(對於某些類型)
- 難度控制:能夠生成不同難度級別的謎題
- 生成效率:在合理時間內完成謎題生成
- 品質保證:避免平凡或過於簡單的解決方案
為什麼需要理解謎題生成演算法?
- 遊戲開發:創建動態、可重玩的謎題遊戲
- 教育應用:生成客製化的練習題和測驗
- AI訓練:提供多樣化的訓練數據
- 演算法學習:理解約束滿足和搜索演算法
- 優化技能:學習如何提升演算法效率
本文將深入探討謎題生成的核心演算法,從基礎的回溯法到高級的約束滿足問題,並提供實用的實現技巧和優化策略。
🔄 回溯演算法基礎
回溯演算法是謎題生成的基石,它透過系統性地嘗試所有可能的解決方案,並在遇到無效狀態時回溯到上一步,直到找到有效解。
回溯演算法的核心概念
基本回溯框架
function backtrack(state, depth) {
// 1. 檢查是否達到目標
if (isGoalState(state)) {
return state; // 找到解
}
// 2. 檢查是否超過深度限制
if (depth > MAX_DEPTH) {
return null; // 搜索失敗
}
// 3. 生成所有可能的下一步選擇
const choices = generateChoices(state);
// 4. 嘗試每個選擇
for (const choice of choices) {
// 做出選擇
const newState = makeChoice(state, choice);
// 檢查選擇是否有效
if (isValid(newState)) {
// 遞迴搜索
const result = backtrack(newState, depth + 1);
// 如果找到解,返回
if (result !== null) {
return result;
}
}
// 回溯(撤銷選擇)
// JavaScript 中通過創建新狀態自動實現
}
// 5. 所有選擇都失敗
return null;
}數獨生成器的回溯實現
完整數獨生成器
class SudokuBacktrackGenerator {
constructor() {
this.grid = Array(9).fill(null).map(() => Array(9).fill(0));
}
// 生成完整的數獨解
generate() {
this.fillGrid(0, 0);
return this.grid;
}
// 回溯填充網格
fillGrid(row, col) {
// 到達最後一格,完成
if (row === 9) {
return true;
}
// 計算下一個位置
const nextRow = col === 8 ? row + 1 : row;
const nextCol = col === 8 ? 0 : col + 1;
// 生成隨機數字順序
const numbers = this.shuffleArray([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]);
// 嘗試每個數字
for (const num of numbers) {
if (this.isValidPlacement(row, col, num)) {
// 做出選擇
this.grid[row][col] = num;
// 遞迴填充下一格
if (this.fillGrid(nextRow, nextCol)) {
return true;
}
// 回溯
this.grid[row][col] = 0;
}
}
// 所有數字都不行
return false;
}
// 檢查數字放置是否有效
isValidPlacement(row, col, num) {
// 檢查行
for (let c = 0; c < 9; c++) {
if (this.grid[row][c] === num) return false;
}
// 檢查列
for (let r = 0; r < 9; r++) {
if (this.grid[r][col] === num) return false;
}
// 檢查 3x3 宮格
const boxRow = Math.floor(row / 3) * 3;
const boxCol = Math.floor(col / 3) * 3;
for (let r = boxRow; r < boxRow + 3; r++) {
for (let c = boxCol; c < boxCol + 3; c++) {
if (this.grid[r][c] === num) return false;
}
}
return true;
}
// Fisher-Yates 洗牌算法
shuffleArray(array) {
const arr = [...array];
for (let i = arr.length - 1; i > 0; i--) {
const j = Math.floor(Math.random() * (i + 1));
[arr[i], arr[j]] = [arr[j], arr[i]];
}
return arr;
}
}🎯 回溯演算法優化技巧
- 隨機化選擇順序:避免生成相同的謎題
- 早期失敗檢測:盡快識別無效狀態
- 約束傳播:在做出選擇時立即檢查相關約束
- 啟發式排序:優先嘗試更可能成功的選擇
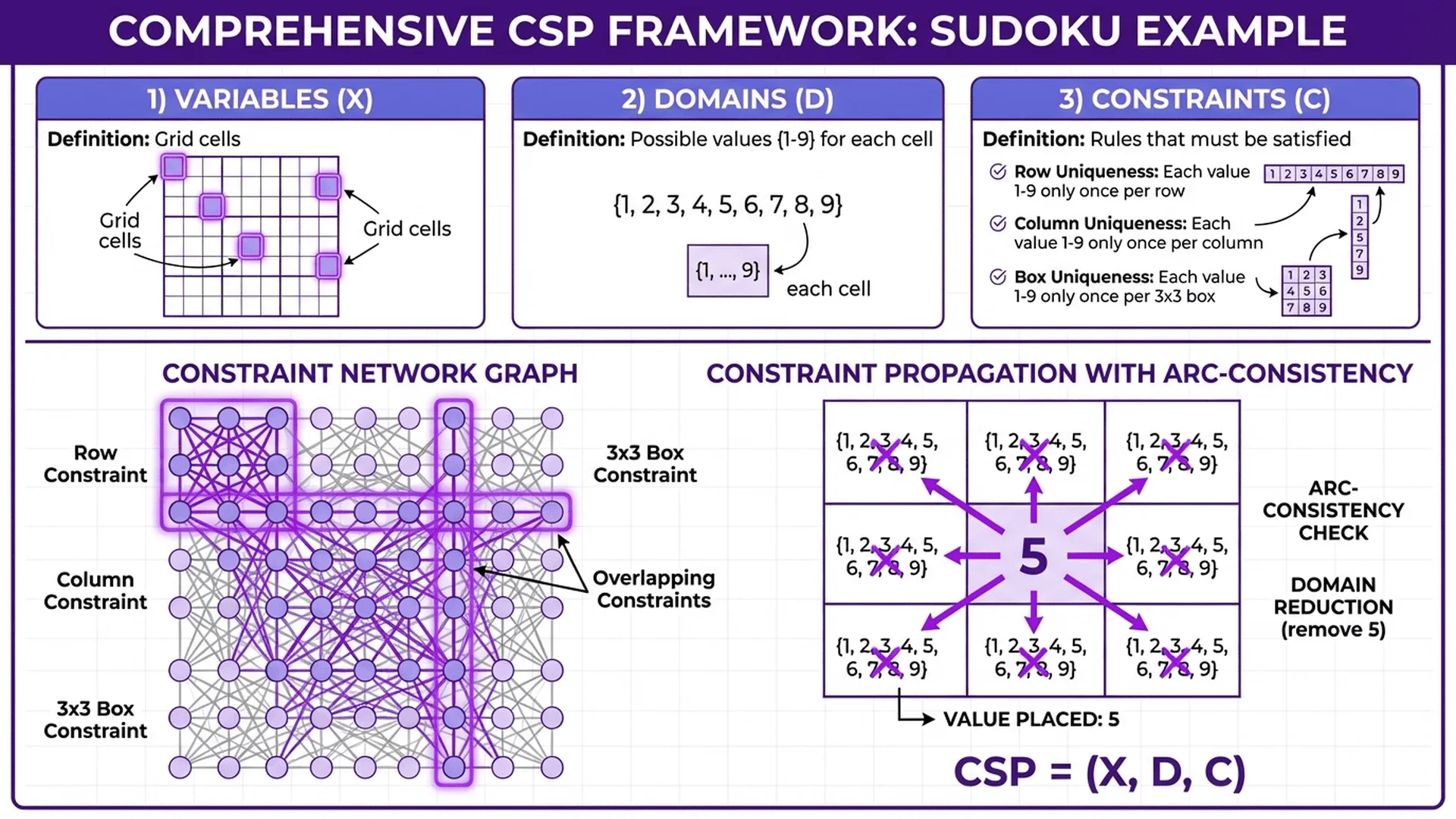
🧩 約束滿足問題(CSP)
約束滿足問題(Constraint Satisfaction Problem, CSP)是一種更通用的問題建模方法,它將謎題生成形式化為變數、域和約束的組合。
CSP 的組成要素
📋 CSP 三要素
- 變數(Variables):需要賦值的對象(如數獨中的每個格子)
- 域(Domains):每個變數可能的取值範圍(如 1-9)
- 約束(Constraints):變數之間的限制關係(如同行不重複)
CSP 求解器實現
通用 CSP 求解器
class CSPSolver {
constructor(variables, domains, constraints) {
this.variables = variables;
this.domains = domains;
this.constraints = constraints;
this.assignment = {};
}
// 主求解方法
solve() {
return this.backtrackSearch({});
}
// 回溯搜索
backtrackSearch(assignment) {
// 所有變數都已賦值
if (Object.keys(assignment).length === this.variables.length) {
return assignment;
}
// 選擇下一個變數(MRV 啟發式)
const variable = this.selectUnassignedVariable(assignment);
// 獲取變數的域值(LCV 啟發式)
const values = this.orderDomainValues(variable, assignment);
// 嘗試每個值
for (const value of values) {
if (this.isConsistent(variable, value, assignment)) {
// 做出選擇
assignment[variable] = value;
// 前向檢查和約束傳播
const inferences = this.inference(variable, value, assignment);
if (inferences !== null) {
// 遞迴求解
const result = this.backtrackSearch(assignment);
if (result !== null) {
return result;
}
}
// 回溯
delete assignment[variable];
this.restoreInferences(inferences);
}
}
return null;
}
// MRV(最少剩餘值)啟發式
selectUnassignedVariable(assignment) {
let minVariable = null;
let minCount = Infinity;
for (const variable of this.variables) {
if (!(variable in assignment)) {
const count = this.countLegalValues(variable, assignment);
if (count < minCount) {
minCount = count;
minVariable = variable;
}
}
}
return minVariable;
}
// LCV(最少約束值)啟發式
orderDomainValues(variable, assignment) {
const values = [...this.domains[variable]];
// 按照限制其他變數的程度排序
values.sort((a, b) => {
const constraintsA = this.countConstraints(variable, a, assignment);
const constraintsB = this.countConstraints(variable, b, assignment);
return constraintsA - constraintsB;
});
return values;
}
// 檢查賦值是否一致
isConsistent(variable, value, assignment) {
for (const constraint of this.constraints) {
if (!constraint.isSatisfied(variable, value, assignment)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
// 前向檢查和 AC-3 約束傳播
inference(variable, value, assignment) {
const inferences = {};
// 對每個相關變數
for (const neighbor of this.getNeighbors(variable)) {
if (!(neighbor in assignment)) {
// 從鄰居的域中移除不一致的值
const removedValues = [];
for (const neighborValue of this.domains[neighbor]) {
if (!this.isConsistent(neighbor, neighborValue,
{...assignment, [variable]: value})) {
removedValues.push(neighborValue);
}
}
// 如果域為空,失敗
if (removedValues.length === this.domains[neighbor].length) {
return null;
}
inferences[neighbor] = removedValues;
}
}
return inferences;
}
// 獲取相關變數
getNeighbors(variable) {
const neighbors = new Set();
for (const constraint of this.constraints) {
if (constraint.involves(variable)) {
neighbors.add(...constraint.getOtherVariables(variable));
}
}
return Array.from(neighbors);
}
// 計算合法值數量
countLegalValues(variable, assignment) {
let count = 0;
for (const value of this.domains[variable]) {
if (this.isConsistent(variable, value, assignment)) {
count++;
}
}
return count;
}
// 計算約束數量
countConstraints(variable, value, assignment) {
let count = 0;
const testAssignment = {...assignment, [variable]: value};
for (const neighbor of this.getNeighbors(variable)) {
if (!(neighbor in assignment)) {
for (const neighborValue of this.domains[neighbor]) {
if (!this.isConsistent(neighbor, neighborValue, testAssignment)) {
count++;
}
}
}
}
return count;
}
// 恢復推論
restoreInferences(inferences) {
// 實現推論恢復邏輯
}
}🚀 CSP 優化策略
- 變數排序:MRV(最少剩餘值)優先選擇約束最多的變數
- 值排序:LCV(最少約束值)優先嘗試約束最少的值
- 前向檢查:立即檢測不一致並剪枝
- AC-3 算法:強制弧一致性,提前發現衝突
📊 難度評估技術
生成不同難度的謎題是謎題生成器的關鍵功能。難度評估需要考慮多個因素,從表面特徵到求解複雜度。
難度評估的多維度方法
🎯 難度評估因素
- 提示數量:給定的初始線索數量
- 求解技巧:需要使用的解題技巧類型
- 分支因子:每步選擇的平均數量
- 搜索深度:找到解需要的步驟數
- 對稱性:謎題的對稱模式
- 回溯次數:求解器回溯的次數
數獨難度評估器
智能難度評估系統
class SudokuDifficultyAssessor {
constructor(puzzle) {
this.puzzle = puzzle;
this.techniques = {
nakedSingle: 1,
hiddenSingle: 2,
nakedPair: 3,
hiddenPair: 4,
pointing: 5,
xWing: 7,
swordfish: 8,
xyWing: 9,
coloring: 10
};
}
// 評估難度
assessDifficulty() {
const metrics = {
clueCount: this.countClues(),
requiredTechniques: this.analyzeRequiredTechniques(),
branchingFactor: this.calculateBranchingFactor(),
symmetry: this.checkSymmetry(),
backtrackCount: this.countBacktracks()
};
const difficulty = this.calculateOverallDifficulty(metrics);
return {
level: this.getDifficultyLevel(difficulty),
score: difficulty,
metrics: metrics,
explanation: this.generateExplanation(metrics)
};
}
// 計算線索數量
countClues() {
let count = 0;
for (let row = 0; row < 9; row++) {
for (let col = 0; col < 9; col++) {
if (this.puzzle[row][col] !== 0) {
count++;
}
}
}
return count;
}
// 分析需要的解題技巧
analyzeRequiredTechniques() {
const usedTechniques = [];
const solver = new SudokuSolver(this.puzzle);
// 嘗試使用不同技巧求解
if (solver.tryNakedSingles()) {
usedTechniques.push('nakedSingle');
}
if (solver.tryHiddenSingles()) {
usedTechniques.push('hiddenSingle');
}
if (solver.tryNakedPairs()) {
usedTechniques.push('nakedPair');
}
if (solver.tryXWing()) {
usedTechniques.push('xWing');
}
// 計算最高技巧難度
let maxDifficulty = 0;
for (const technique of usedTechniques) {
if (this.techniques[technique] > maxDifficulty) {
maxDifficulty = this.techniques[technique];
}
}
return {
techniques: usedTechniques,
maxDifficulty: maxDifficulty
};
}
// 計算分支因子
calculateBranchingFactor() {
let totalChoices = 0;
let emptyCells = 0;
for (let row = 0; row < 9; row++) {
for (let col = 0; col < 9; col++) {
if (this.puzzle[row][col] === 0) {
emptyCells++;
totalChoices += this.countPossibleValues(row, col);
}
}
}
return emptyCells > 0 ? totalChoices / emptyCells : 0;
}
// 計算可能值數量
countPossibleValues(row, col) {
const possible = new Set([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]);
// 移除行中的值
for (let c = 0; c < 9; c++) {
possible.delete(this.puzzle[row][c]);
}
// 移除列中的值
for (let r = 0; r < 9; r++) {
possible.delete(this.puzzle[r][col]);
}
// 移除宮格中的值
const boxRow = Math.floor(row / 3) * 3;
const boxCol = Math.floor(col / 3) * 3;
for (let r = boxRow; r < boxRow + 3; r++) {
for (let c = boxCol; c < boxCol + 3; c++) {
possible.delete(this.puzzle[r][c]);
}
}
return possible.size;
}
// 檢查對稱性
checkSymmetry() {
// 檢查 180° 旋轉對稱
let rotation180 = true;
for (let row = 0; row < 9; row++) {
for (let col = 0; col < 9; col++) {
const oppositeRow = 8 - row;
const oppositeCol = 8 - col;
const cell1 = this.puzzle[row][col];
const cell2 = this.puzzle[oppositeRow][oppositeCol];
if ((cell1 === 0) !== (cell2 === 0)) {
rotation180 = false;
break;
}
}
if (!rotation180) break;
}
return rotation180 ? 'rotation180' : 'none';
}
// 計算回溯次數
countBacktracks() {
const solver = new SudokuBacktrackSolver(this.puzzle);
return solver.solveWithBacktrackCount();
}
// 計算整體難度
calculateOverallDifficulty(metrics) {
let score = 0;
// 線索數量影響(線索越少越難)
score += (81 - metrics.clueCount) * 0.5;
// 技巧難度影響
score += metrics.requiredTechniques.maxDifficulty * 10;
// 分支因子影響
score += metrics.branchingFactor * 5;
// 回溯次數影響
score += Math.log(metrics.backtrackCount + 1) * 3;
// 對稱性影響(對稱謎題通常更簡單)
if (metrics.symmetry !== 'none') {
score -= 5;
}
return score;
}
// 獲取難度級別
getDifficultyLevel(score) {
if (score < 20) return 'Easy';
if (score < 40) return 'Medium';
if (score < 60) return 'Hard';
if (score < 80) return 'Expert';
return 'Evil';
}
// 生成解釋
generateExplanation(metrics) {
const parts = [];
parts.push(`線索數量: ${metrics.clueCount}/81`);
parts.push(`需要技巧: ${metrics.requiredTechniques.techniques.join(', ')}`);
parts.push(`平均分支因子: ${metrics.branchingFactor.toFixed(2)}`);
parts.push(`回溯次數: ${metrics.backtrackCount}`);
parts.push(`對稱性: ${metrics.symmetry}`);
return parts.join(' | ');
}
}✅ 唯一解保證方法
許多謎題類型要求有且僅有一個解。保證唯一解是謎題生成中最具挑戰性的部分之一。
唯一解驗證策略
唯一解驗證器
class UniqueSolutionVerifier {
constructor(puzzle) {
this.puzzle = puzzle;
this.solutionCount = 0;
this.maxSolutions = 2; // 只需要知道是否多於1個解
}
// 驗證是否有唯一解
hasUniqueSolution() {
this.solutionCount = 0;
this.countSolutions(this.copyPuzzle(), 0, 0);
return this.solutionCount === 1;
}
// 計算解的數量
countSolutions(grid, row, col) {
// 已找到足夠的解,提前結束
if (this.solutionCount >= this.maxSolutions) {
return;
}
// 找到下一個空格
while (row < 9 && grid[row][col] !== 0) {
col++;
if (col === 9) {
col = 0;
row++;
}
}
// 到達末尾,找到一個解
if (row === 9) {
this.solutionCount++;
return;
}
// 嘗試每個數字
for (let num = 1; num <= 9; num++) {
if (this.isValid(grid, row, col, num)) {
grid[row][col] = num;
this.countSolutions(grid, row, col);
grid[row][col] = 0; // 回溯
}
}
}
// 檢查放置是否有效
isValid(grid, row, col, num) {
// 檢查行
for (let c = 0; c < 9; c++) {
if (grid[row][c] === num) return false;
}
// 檢查列
for (let r = 0; r < 9; r++) {
if (grid[r][col] === num) return false;
}
// 檢查宮格
const boxRow = Math.floor(row / 3) * 3;
const boxCol = Math.floor(col / 3) * 3;
for (let r = boxRow; r < boxRow + 3; r++) {
for (let c = boxCol; c < boxCol + 3; c++) {
if (grid[r][c] === num) return false;
}
}
return true;
}
// 複製謎題
copyPuzzle() {
return this.puzzle.map(row => [...row]);
}
}
// 帶唯一解保證的謎題生成器
class UniquePuzzleGenerator {
generateUniquePuzzle(cluesCount) {
// 1. 生成完整的解
const solution = this.generateCompleteSolution();
// 2. 創建空謎題
const puzzle = solution.map(row => [...row]);
// 3. 隨機移除數字直到達到目標線索數
const cellsToRemove = 81 - cluesCount;
let removed = 0;
// 創建所有格子的列表
const cells = [];
for (let r = 0; r < 9; r++) {
for (let c = 0; c < 9; c++) {
cells.push([r, c]);
}
}
// 隨機打亂格子順序
this.shuffleArray(cells);
// 嘗試移除每個格子
for (const [row, col] of cells) {
if (removed >= cellsToRemove) break;
// 備份當前值
const backup = puzzle[row][col];
puzzle[row][col] = 0;
// 檢查是否仍有唯一解
const verifier = new UniqueSolutionVerifier(puzzle);
if (!verifier.hasUniqueSolution()) {
// 恢復值
puzzle[row][col] = backup;
} else {
removed++;
}
}
return puzzle;
}
// 生成完整解(使用前面的回溯生成器)
generateCompleteSolution() {
const generator = new SudokuBacktrackGenerator();
return generator.generate();
}
// 洗牌
shuffleArray(array) {
for (let i = array.length - 1; i > 0; i--) {
const j = Math.floor(Math.random() * (i + 1));
[array[i], array[j]] = [array[j], array[i]];
}
}
}⚠️ 唯一解驗證的性能考慮
唯一解驗證可能非常耗時,特別是對於線索較少的謎題。優化策略:
- 早期終止:找到第二個解時立即停止
- 對稱性:利用對稱性減少驗證次數
- 智能移除:優先移除約束較強的格子
- 批量驗證:一次移除多個格子再驗證
🚀 演算法優化技巧
謎題生成可能計算密集,特別是對於大型或複雜的謎題。以下是一些關鍵的優化技術。
性能優化策略
💡 優化技術總覽
- 位運算:使用位元來表示域和約束
- 記憶化:快取重複計算的結果
- 啟發式搜索:使用智能策略引導搜索
- 並行化:利用多核心同時生成多個謎題
- 漸進式生成:分階段生成,避免一次性計算
位運算優化實現
使用位運算的高效求解器
class BitBasedSudokuSolver {
constructor(puzzle) {
this.grid = puzzle;
// 使用位元表示每個單元的可能值
// 例如: 0b111111111 表示 1-9 都可能
this.possibilities = Array(9).fill(null)
.map(() => Array(9).fill(0b111111111));
this.initializePossibilities();
}
// 初始化可能性位元
initializePossibilities() {
for (let row = 0; row < 9; row++) {
for (let col = 0; col < 9; col++) {
if (this.grid[row][col] !== 0) {
const num = this.grid[row][col];
this.possibilities[row][col] = 1 << (num - 1);
this.propagateConstraint(row, col, num);
}
}
}
}
// 傳播約束
propagateConstraint(row, col, num) {
const mask = ~(1 << (num - 1));
// 移除行中的可能性
for (let c = 0; c < 9; c++) {
if (c !== col) {
this.possibilities[row][c] &= mask;
}
}
// 移除列中的可能性
for (let r = 0; r < 9; r++) {
if (r !== row) {
this.possibilities[r][col] &= mask;
}
}
// 移除宮格中的可能性
const boxRow = Math.floor(row / 3) * 3;
const boxCol = Math.floor(col / 3) * 3;
for (let r = boxRow; r < boxRow + 3; r++) {
for (let c = boxCol; c < boxCol + 3; c++) {
if (r !== row || c !== col) {
this.possibilities[r][c] &= mask;
}
}
}
}
// 計算位元中設置的位數(可能值數量)
countBits(n) {
let count = 0;
while (n) {
count += n & 1;
n >>= 1;
}
return count;
}
// 獲取位元中最低的設置位(最小的可能值)
getLowestBit(n) {
return n & -n;
}
// 位元到數字
bitToNumber(bit) {
for (let i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
if (bit & (1 << i)) {
return i + 1;
}
}
return 0;
}
// 求解
solve() {
return this.backtrack();
}
// 回溯搜索
backtrack() {
// 找到可能性最少的空格(MRV 啟發式)
let minRow = -1, minCol = -1, minCount = 10;
for (let row = 0; row < 9; row++) {
for (let col = 0; col < 9; col++) {
if (this.grid[row][col] === 0) {
const count = this.countBits(this.possibilities[row][col]);
// 發現矛盾
if (count === 0) {
return false;
}
if (count < minCount) {
minCount = count;
minRow = row;
minCol = col;
}
}
}
}
// 所有格子都填滿,完成
if (minRow === -1) {
return true;
}
// 保存當前狀態
const savedPossibilities = this.savePossibilities();
// 嘗試每個可能的值
let possible = this.possibilities[minRow][minCol];
while (possible) {
const bit = this.getLowestBit(possible);
const num = this.bitToNumber(bit);
// 做出選擇
this.grid[minRow][minCol] = num;
this.possibilities[minRow][minCol] = bit;
this.propagateConstraint(minRow, minCol, num);
// 遞迴求解
if (this.backtrack()) {
return true;
}
// 回溯
this.restorePossibilities(savedPossibilities);
this.grid[minRow][minCol] = 0;
// 移除已嘗試的位元
possible &= ~bit;
}
return false;
}
// 保存可能性狀態
savePossibilities() {
return this.possibilities.map(row => [...row]);
}
// 恢復可能性狀態
restorePossibilities(saved) {
for (let row = 0; row < 9; row++) {
for (let col = 0; col < 9; col++) {
this.possibilities[row][col] = saved[row][col];
}
}
}
}🎯 實戰優化建議
- 選擇合適的數據結構:使用位元、哈希表等高效結構
- 減少冗餘計算:快取和記憶化重複結果
- 智能剪枝:盡早識別無效分支
- 使用啟發式:MRV、LCV 等引導搜索
- 分段驗證:在生成過程中逐步驗證,而非最後驗證
🎓 結論與資源
關鍵要點總結
- 回溯演算法是基礎:理解回溯是掌握謎題生成的第一步
- CSP 提供通用框架:約束滿足問題可以建模各種謎題
- 難度評估需多維度:綜合考慮多個因素才能準確評估
- 唯一解驗證很重要:但要注意性能影響
- 優化是持續過程:從位運算到並行化,都能提升性能
進階學習資源
📚 推薦書籍
- Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach - Russell & Norvig
- Algorithm Design Manual - Steven Skiena
- Heuristics: Intelligent Search Strategies - Judea Pearl
🔗 線上資源
- Constraint Programming (Wikipedia)
- CSP-Solver GitHub 專案
- Algorithm Visualizations (VisuAlgo)