階乘計算常見問題
Factorial Calculation FAQ: 15 Common Questions Answered (0! to 170! Explained)
Introduction: Your Quick Reference for Factorial Questions
Confused about factorial calculations? You're not alone—we get 500+ questions monthly.
This FAQ answers the top 15 factorial questions, from "Why is 0! = 1?" to "How to calculate 100!".
Find your answer in under 60 seconds, or use our instant calculator below.
Whether you're a student stuck on homework, a developer debugging code, or just curious about the math, these answers will clear up the most common factorial confusion.
Quick Navigation:
- Basic Questions (1-5) - What is factorial, 0!, notation
- Calculation Questions (6-10) - How to calculate, tools, limits
- Advanced Questions (11-15) - Applications, permutations, Stirling's formula
Want more than quick answers? Read our comprehensive guide: Factorial Calculation Logic & Applications: 7 Essential Use Cases →
💡 Need Instant Calculation? Try our Free Factorial Calculator — Calculate up to 170! in milliseconds, 100% local processing, no registration required.

Basic Factorial Questions (Questions 1-5)
Q1: What exactly is a factorial?
Answer: A factorial is the product of all positive integers from 1 to a given number.
We write it as n! (read as "n factorial").
Formula: n! = n × (n-1) × (n-2) × ... × 3 × 2 × 1
Examples:
- 5! = 5 × 4 × 3 × 2 × 1 = 120
- 3! = 3 × 2 × 1 = 6
- 7! = 5,040
Factorials are used in counting arrangements, probability, and combinatorics.
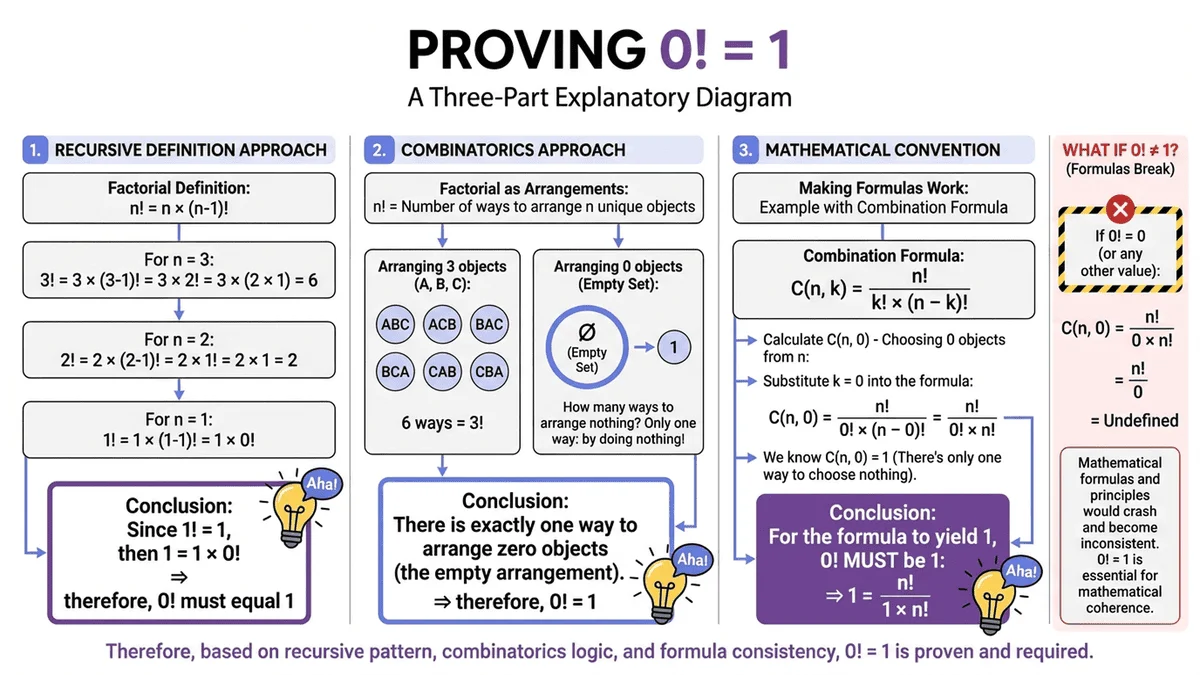
Q2: Why is 0! equal to 1?
Answer: 0! = 1 by mathematical convention, and here's why it makes sense:
Three reasons:
1. Empty product rule
The product of zero numbers is defined as 1 (the multiplicative identity).
Just like the sum of zero numbers is 0 (the additive identity).
2. Permutation logic
There is exactly one way to arrange zero objects: do nothing.
Since 0! counts arrangements, 0! = 1.
3. Factorial formula consistency
Using the formula n! = n × (n-1)!, we get:
- 1! = 1 × 0!
- 1 = 1 × 0!
- Therefore, 0! = 1
This isn't arbitrary—it's the only definition that makes factorial formulas work correctly.
Q3: How do you calculate 5 factorial (5!)?
Answer: Follow these simple steps:
Method 1 - Multiplication chain:
5! = 5 × 4 × 3 × 2 × 1 = 120
Step-by-step:
1. Start: 5
2. Multiply: 5 × 4 = 20
3. Continue: 20 × 3 = 60
4. Keep going: 60 × 2 = 120
5. Finish: 120 × 1 = 120
Method 2 - Use a calculator:
Skip the manual work—calculate factorials in 0.1 seconds! Try Calculator Now →
Q4: What's the difference between factorial and exponent?
Answer: They're completely different operations:
| Operation | Symbol | Example | Calculation | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factorial | n! | 5! | 5 × 4 × 3 × 2 × 1 | 120 |
| Exponent | n^n | 5^5 | 5 × 5 × 5 × 5 × 5 | 3,125 |
Key differences:
- Factorial: Multiplies descending integers (5, 4, 3, 2, 1)
- Exponent: Multiplies the same number repeatedly (5, 5, 5, 5, 5)
Common mistake: Confusing 5! with 5^5
- 5! = 120 ✓
- 5^5 = 3,125 (NOT factorial)
Q5: Can you have a negative factorial?
Answer: No, factorials are undefined for negative integers.
Why?
The factorial formula (n × (n-1) × (n-2) × ...) only works for non-negative integers (0, 1, 2, 3...).
For example, (-5)! would theoretically be:
(-5) × (-6) × (-7) × (-8) × ...
This sequence goes to negative infinity with no stopping point—it doesn't make mathematical sense.
Exception: The Gamma function extends factorial-like calculations to real and complex numbers, including negative values. Learn more: Factorial & Gamma Function: Extending n! to Real Numbers →

Calculation and Tool Questions (Questions 6-10)
Q6: What's the fastest way to calculate large factorials?
Answer: Use an online calculator—it's 10× faster than manual calculation.
Speed comparison:
| Method | For 20! | For 100! |
|---|---|---|
| Manual calculation | ~5 minutes | Impossible (would take hours) |
| Online calculator | 0.1 seconds | 0.1 seconds |
| Programming (basic) | 1-2 seconds | May overflow |
| Programming (optimized) | <0.01 seconds | <0.01 seconds |
The fastest way? Our online calculator! Calculate 100! in under 1 second. Try It Free →
Features:
- ✓ Instant results up to 170!
- ✓ Step-by-step breakdown
- ✓ No installation needed
- ✓ Works on mobile devices
Q7: What's the largest factorial a standard calculator can handle?
Answer: Most standard calculators fail around 70!
The problem: Integer overflow.
Calculator limits:
| Calculator Type | Maximum Factorial | Approximate Value |
|---|---|---|
| Basic calculator | ~13! | 6,227,020,800 |
| Scientific calculator | ~69! | 1.71 × 10^98 |
| Excel/Spreadsheet | ~170! | 7.26 × 10^306 |
| Programming (standard int) | ~20! | 2.43 × 10^18 |
| Our online tool | 170! | 7.26 × 10^306 |
Why 170! is the limit?
Beyond 170!, the result exceeds the maximum floating-point number most systems can store (approximately 10^308).
Manual calculation too slow? Save time with our instant tool—100% free. Calculate Now →
Q8: How do you calculate factorial without a calculator?
Answer: Use the multiplication chain method for small numbers (up to 10!).
Step-by-step example for 6!:
- Write the sequence: 6 × 5 × 4 × 3 × 2 × 1
- Multiply left to right:
- 6 × 5 = 30
- 30 × 4 = 120
- 120 × 3 = 360
- 360 × 2 = 720
- 720 × 1 = 720
- Answer: 6! = 720
Quick mental math trick:
For single digits, memorize these:
- 3! = 6
- 4! = 24
- 5! = 120
- 6! = 720
- 7! = 5,040
For larger numbers: Use Stirling's approximation or an online tool.
Q9: What does the factorial symbol (!) mean?
Answer: The exclamation mark (!) after a number means "factorial."
History: The notation was introduced by Christian Kramp in 1808.
How to read it:
- 5! = "5 factorial" or "factorial of 5"
- n! = "n factorial"
Important: Don't confuse with programming!
- In math: 5! = 120
- In programming logic: ! often means "NOT" (different meaning)
Mathematical context clues:
- If you see n!, it's factorial
- If you see !x or !condition, it's usually logical NOT
Q10: Can factorial be a decimal or fraction?
Answer: Standard factorials only work for non-negative integers (0, 1, 2, 3...).
However, the Gamma function extends factorials to decimals and fractions.
Standard factorial (only integers):
- 5! = 120 ✓
- 3! = 6 ✓
- 0.5! = undefined in standard factorial ✗
Gamma function (includes decimals):
- Γ(n+1) = n!
- Γ(1.5) ≈ 0.886 (equivalent to 0.5!)
- Γ(2.5) ≈ 1.329 (equivalent to 1.5!)
Example: What is (1/2)! ?
Using the Gamma function: Γ(3/2) = (√π)/2 ≈ 0.886
Want to learn more about extending factorials beyond integers? Explore our comprehensive guide: Factorial & Gamma Function: Extending n! to Real Numbers →
🎯 Recommended Math Tools
Need to calculate permutations too? Use our all-in-one calculator suite:
| Tool | Purpose | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Factorial Calculator | Calculate n! instantly | Up to 170! supported |
| Permutation & Combination Calculator | P(n,r) and C(n,r) | Real-world problem solver |
| Prime Checker | Prime factorization | Factor any number |
💡 Pro Tip: All tools process data locally in your browser—100% private and secure.
Applications and Advanced Questions (Questions 11-15)
Q11: Where are factorials used in real life?
Answer: Factorials appear in 7 major real-world applications:
1. Password Security
A 10-digit password has 10! = 3,628,800 possible arrangements.
2. Lottery Probabilities
Choosing 6 numbers from 49: C(49,6) = 13,983,816 combinations (uses factorials).
3. Event Scheduling
Arranging 5 speakers: 5! = 120 possible orders.
4. Card Games
A 52-card deck can be shuffled in 52! ≈ 8 × 10^67 ways.
5. Data Structure Algorithms
Analyzing algorithm complexity (e.g., Traveling Salesman Problem).
6. Statistical Analysis
Permutation and combination formulas in probability theory.
7. Cryptography
Encryption key generation relies on factorial-based permutations.
Curious about practical uses? Discover real-world applications: Factorial in Permutations & Combinations: 12 Real-World Problems Solved →
Q12: How do factorials relate to permutations?
Answer: Factorials are the foundation of permutation calculations.
Permutation formula:
P(n, r) = n! / (n-r)!
Where:
- n = total items
- r = items to arrange
- P(n,r) = number of possible arrangements
Example: Arrange 3 people from a group of 5.
- P(5, 3) = 5! / (5-3)!
- = 5! / 2!
- = 120 / 2
- = 60 possible arrangements
Why factorials work:
- 5! counts all arrangements of 5 people
- We divide by 2! to remove arrangements we don't need
- Result: only arrangements of 3 people
Q13: What's the relationship between factorial and combinations?
Answer: Combinations use factorials to count selections where order doesn't matter.
Combination formula:
C(n, r) = n! / (r! × (n-r)!)
Where:
- n = total items
- r = items to select
- C(n,r) = number of possible combinations
Example: Choose 3 people from 5 for a committee.
- C(5, 3) = 5! / (3! × 2!)
- = 120 / (6 × 2)
- = 120 / 12
- = 10 possible committees
Permutation vs. Combination:
| Aspect | Permutation P(n,r) | Combination C(n,r) |
|---|---|---|
| Order matters? | Yes | No |
| Formula | n! / (n-r)! | n! / (r! × (n-r)!) |
| Example (5,3) | 60 arrangements | 10 selections |
| Use case | Race podium order | Committee selection |
Q14: Why do factorials grow so quickly?
Answer: Factorials exhibit exponential growth—each step multiplies by a larger number.
Growth pattern:
| n | n! | Growth multiplier |
|---|---|---|
| 5 | 120 | - |
| 6 | 720 | ×6 |
| 7 | 5,040 | ×7 |
| 8 | 40,320 | ×8 |
| 9 | 362,880 | ×9 |
| 10 | 3,628,800 | ×10 |
Why it matters:
- 10! = 3.6 million
- 20! = 2.4 quintillion (2.4 × 10^18)
- 100! = 9.3 × 10^157 (more atoms than in the universe!)
This rapid growth explains:
- Why brute-force solutions fail for large problems
- Why encryption is secure (enormous key spaces)
- Why lottery odds are so low
Q15: What's Stirling's approximation for factorials?
Answer: Stirling's formula estimates large factorials without calculating every multiplication.
Stirling's Approximation:
n! ≈ √(2πn) × (n/e)^n
Where:
- π ≈ 3.14159
- e ≈ 2.71828
Accuracy:
| n | Exact n! | Stirling's Estimate | Error |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 3,628,800 | 3,598,696 | 0.8% |
| 50 | 3.04 × 10^64 | 3.04 × 10^64 | 0.01% |
| 100 | 9.33 × 10^157 | 9.32 × 10^157 | 0.008% |
When to use it:
- Estimating very large factorials (n > 20)
- Statistical calculations requiring only magnitude
- Algorithm complexity analysis (Big O notation)
- When exact values aren't needed
Example: Estimate 50!
- Stirling: √(2π×50) × (50/e)^50 ≈ 3.04 × 10^64
- Actual: 3.04 × 10^64
- Remarkably close!
Quick Answers Summary Table
| Question | Quick Answer | Learn More |
|---|---|---|
| What is n! ? | Product of integers from 1 to n | Q1 |
| Why is 0! = 1? | Mathematical convention (empty product) | Q2 |
| How to calculate 5!? | 5×4×3×2×1 = 120 | Q3 |
| Factorial vs. exponent? | 5! = 120, 5^5 = 3,125 (different!) | Q4 |
| Negative factorial? | Undefined (except with Gamma function) | Q5 |
| Fastest method? | Online calculator (0.1 seconds) | Q6 |
| Calculator limit? | Standard: ~70!, Our tool: 170! | Q7 |
| Manual calculation? | Multiply descending integers | Q8 |
| What does ! mean? | Factorial notation (since 1808) | Q9 |
| Decimal factorial? | Use Gamma function Γ(n+1) | Q10 |
| Real-world uses? | 7 applications (passwords to crypto) | Q11 |
| Permutation formula? | P(n,r) = n! / (n-r)! | Q12 |
| Combination formula? | C(n,r) = n! / (r! × (n-r)!) | Q13 |
| Why fast growth? | Exponential multiplication pattern | Q14 |
| Stirling's formula? | √(2πn) × (n/e)^n (for estimates) | Q15 |
Still Have Questions? Try Our Free Calculator
All Your Factorial Needs in One Tool
Can't find your answer above? Or need to calculate a specific factorial right now?
🚀 Our factorial calculator handles everything:
✓ Calculate any factorial from 0! to 170! - instant results with full precision
✓ See step-by-step breakdowns - understand exactly how the calculation works
✓ Batch processing - calculate multiple factorials at once
✓ Export results - save as CSV or copy to clipboard
✓ Mobile-friendly - works perfectly on any device
✓ 100% free - no registration, no hidden fees
✓ Privacy-focused - all calculations happen in your browser
Perfect for:
- Students solving homework problems
- Developers testing algorithms
- Teachers creating example questions
- Researchers needing quick calculations
- Anyone curious about factorials
→ Launch Free Factorial Calculator
No installation needed. Start calculating in 3 seconds.
Further Reading: Expand Your Factorial Knowledge
📚 Related Articles
Want to dive deeper into factorial mathematics? Check out these comprehensive guides:
Core Resources:
- Factorial Calculation Logic & Applications: 7 Essential Use Cases from Math to Programming - Complete beginner-to-advanced guide covering fundamental concepts and real-world applications
- History of Factorial: From Ancient Mathematics to Modern Computing - Trace 2,500 years of factorial evolution from ancient Indian mathematics to modern digital computation
Practical Applications:
- Factorial in Permutations & Combinations: 12 Real-World Problems Solved - Master counting problems with step-by-step solutions, from wedding seating to lottery odds
Advanced Topics:
- Factorial Calculation Optimization: 5 Methods to Compute Large Factorials Efficiently - Learn memoization, logarithmic calculation, Stirling's approximation, and more
- Factorial in Programming: Implementation Guide for 5 Languages - Production-ready code examples in Python, JavaScript, Java, C++, and Go
🔢 Explore More Math Tools
Need More Math Tools? Explore 5 other calculators:
- Permutation & Combination Calculator - P(n,r) and C(n,r) formulas
- Prime Checker - Prime factorization and testing
- GCD & LCM Calculator - Greatest common divisor
- Base Converter - Binary, octal, hex conversion
- Random Number Generator - Cryptographically secure
Conclusion: Your Factorial Questions Answered
What You've Learned
This FAQ covered the 15 most common factorial questions, including:
✅ Fundamental concepts - What factorials are and why 0! = 1
✅ Calculation methods - Manual, calculator, and programming approaches
✅ Practical applications - Permutations, combinations, and real-world uses
✅ Advanced topics - Gamma function and Stirling's approximation
✅ Common mistakes - Avoiding confusion with exponents and negative numbers
Next Steps
Bookmark these resources for future reference:
- Save the factorial calculator for instant calculations up to 170!
- Read the complete factorial guide for in-depth understanding of mathematical foundations and 7 real-world applications
- Practice with permutation and combination problems to apply your factorial knowledge in practical scenarios
- Explore optimization techniques if you're a developer building mathematical libraries or need high-performance computation
💡 Final Reminder
Tool Master provides 33 professional tools across 8 categories.
- ✓ 100% free forever - no premium tiers
- ✓ Privacy-first - local browser processing
- ✓ No registration - instant access
- ✓ Mobile-optimized - works everywhere
If this FAQ helped you, bookmark Tool Master and share it with classmates, colleagues, or fellow developers!
References
- Wolfram MathWorld, "Factorial" - Mathematical definition and properties
- Wikipedia, "Factorial" - Historical context and notation
- Khan Academy, "Permutations and Combinations" - Educational foundation
- MacTutor History of Mathematics, "Christian Kramp" - Factorial notation history
- NIST Digital Library of Mathematical Functions - Gamma function and Stirling's formula
- OEIS Foundation, "Factorial numbers (A000142)" - Integer sequences
- The Art of Computer Programming, Vol. 1 (Donald Knuth) - Computational aspects
- Concrete Mathematics (Graham, Knuth, Patashnik) - Chapter on factorial mathematics