10分鐘學會質數檢測
Learn Prime Number Check in 10 Minutes: Beginner's Quick Start Guide 2025
Can you really learn prime number checking in just 10 minutes? Absolutely! Whether you're a student struggling with math homework, a coding beginner, or just curious about numbers, this step-by-step guide will teach you everything you need to know about prime numbers—fast.
By the end of this 10-minute tutorial, you'll be able to:
- ✅ Identify prime numbers instantly
- ✅ Use the quickest manual checking methods
- ✅ Write simple code to check any number
- ✅ Use professional online tools like Tool Master's Prime Checker
- ✅ Avoid common beginner mistakes
Let's dive in! ⏱️
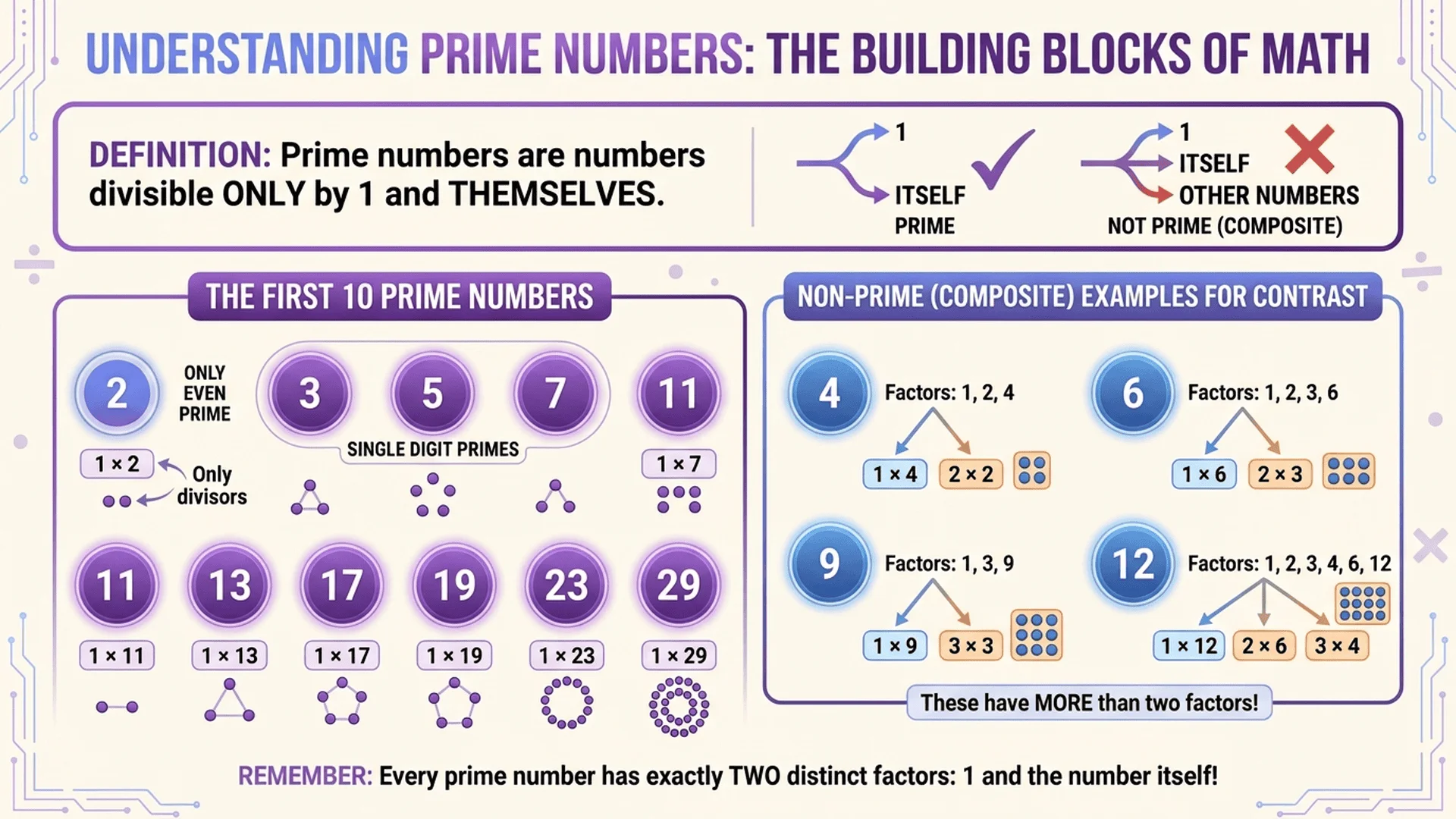
Minutes 1-2: What Are Prime Numbers? (The Basics)
The Simple Definition
A prime number is a whole number greater than 1 that can only be divided evenly by 1 and itself.
Examples:
- ✅ 2 is prime (only divisible by 1 and 2)
- ✅ 7 is prime (only divisible by 1 and 7)
- ✅ 13 is prime (only divisible by 1 and 13)
Non-examples:
- ❌ 4 is NOT prime (divisible by 1, 2, and 4)
- ❌ 9 is NOT prime (divisible by 1, 3, and 9)
- ❌ 1 is NOT prime (special case: not considered prime by mathematicians)
Why Should You Care?
Prime numbers are everywhere:
- 🔐 Internet Security: Every time you buy something online, primes protect your credit card
- 🎮 Gaming: Random number generation in games
- 📱 Apps: Hash tables and data structures
- 🧮 Math Class: Essential for understanding factors and multiples
Key Takeaway: If a number has any divisors other than 1 and itself, it's NOT prime!
For a comprehensive understanding of prime numbers, check our Prime Number Check Complete Guide which covers everything from basics to advanced algorithms.
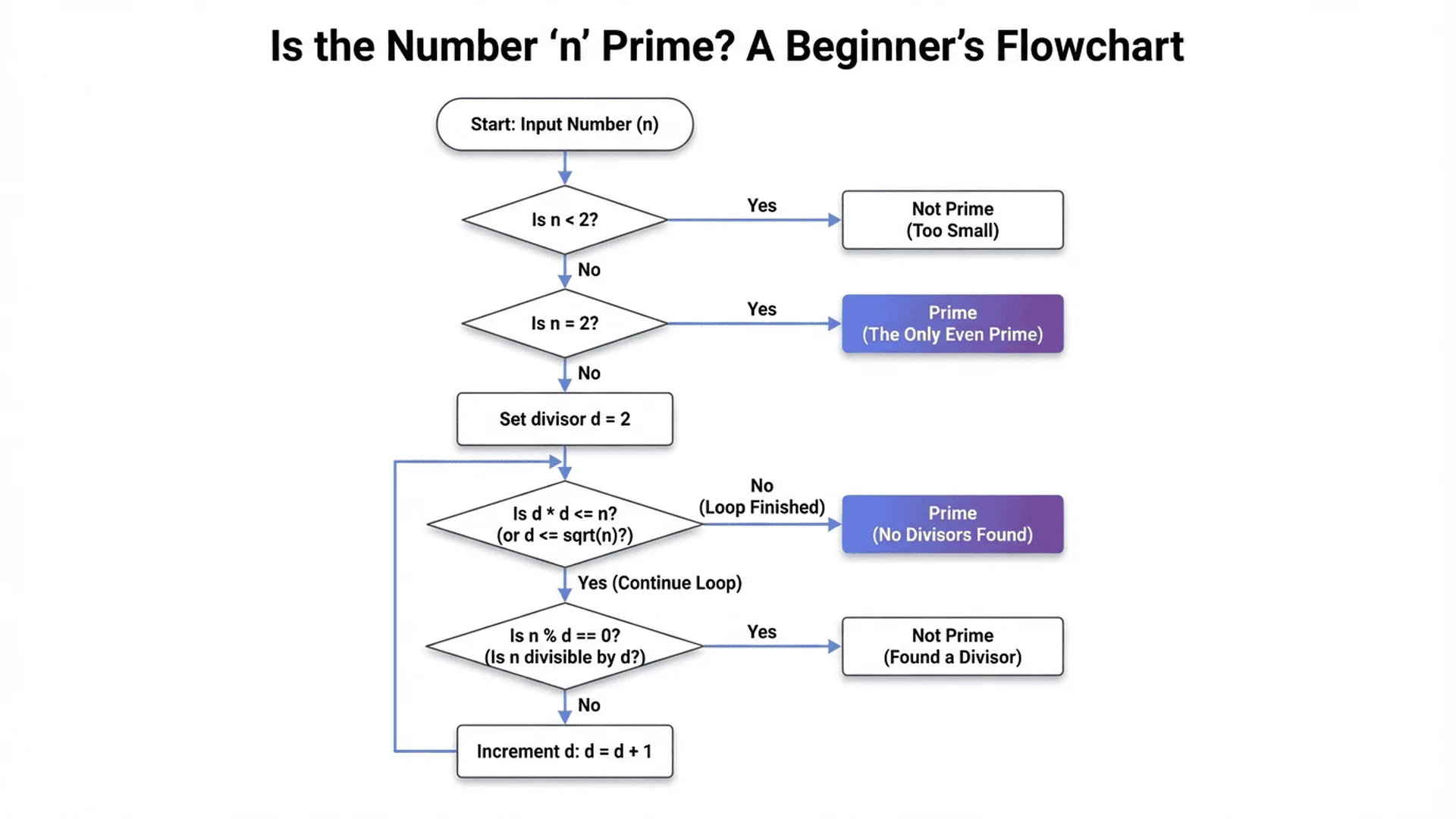
Minutes 3-4: The Fastest Manual Method (For Small Numbers)
Want to check if a number is prime without a computer? Here's the quickest method:
The √n Division Rule
Rule: To check if number n is prime, test if it's divisible by any number from 2 up to √n.
Why it works: If n has a factor larger than √n, it must also have a corresponding factor smaller than √n.
Step-by-Step Example: Is 29 Prime?
Step 1: Calculate √29 ≈ 5.4 → Test divisors 2, 3, 4, 5
Step 2: Check each divisor:
- 29 ÷ 2 = 14.5 (not evenly divisible) ✅
- 29 ÷ 3 = 9.67 (not evenly divisible) ✅
- 29 ÷ 4 = 7.25 (not evenly divisible) ✅
- 29 ÷ 5 = 5.8 (not evenly divisible) ✅
Step 3: No divisors found → 29 is PRIME! 🎉
Quick Practice
Try these yourself (answers at the bottom):
1. Is 17 prime?
2. Is 21 prime?
3. Is 37 prime?
Minutes 5-6: The Easiest Way – Use an Online Tool
Reality check: Manual calculation is great for learning, but for practical use, why not use a free tool?
Why Tool Master's Prime Checker Wins
Try Our Prime Number Checker →
What makes it perfect for beginners:
- ⚡ Instant results – Check numbers up to 10^15 in milliseconds
- 🔒 100% private – All calculations happen in your browser
- 📱 Works everywhere – Phone, tablet, or computer
- 🆓 Completely free – No signup, no limits
- 🎓 Educational – Shows you WHY a number is or isn't prime
How to use it:
1. Go to Tool Master Prime Checker
2. Enter your number (e.g., 97)
3. Click "Check"
4. Get instant answer + explanation
Want to compare different prime checking tools? Read our Best Online Prime Checkers Review to see how Tool Master stacks up against competitors.
Real user testimonial:
"I used to spend 10 minutes checking each number for my math homework. This tool saved me hours!" – Sarah, 10th grade student
Pro tip: Bookmark this tool for homework help!
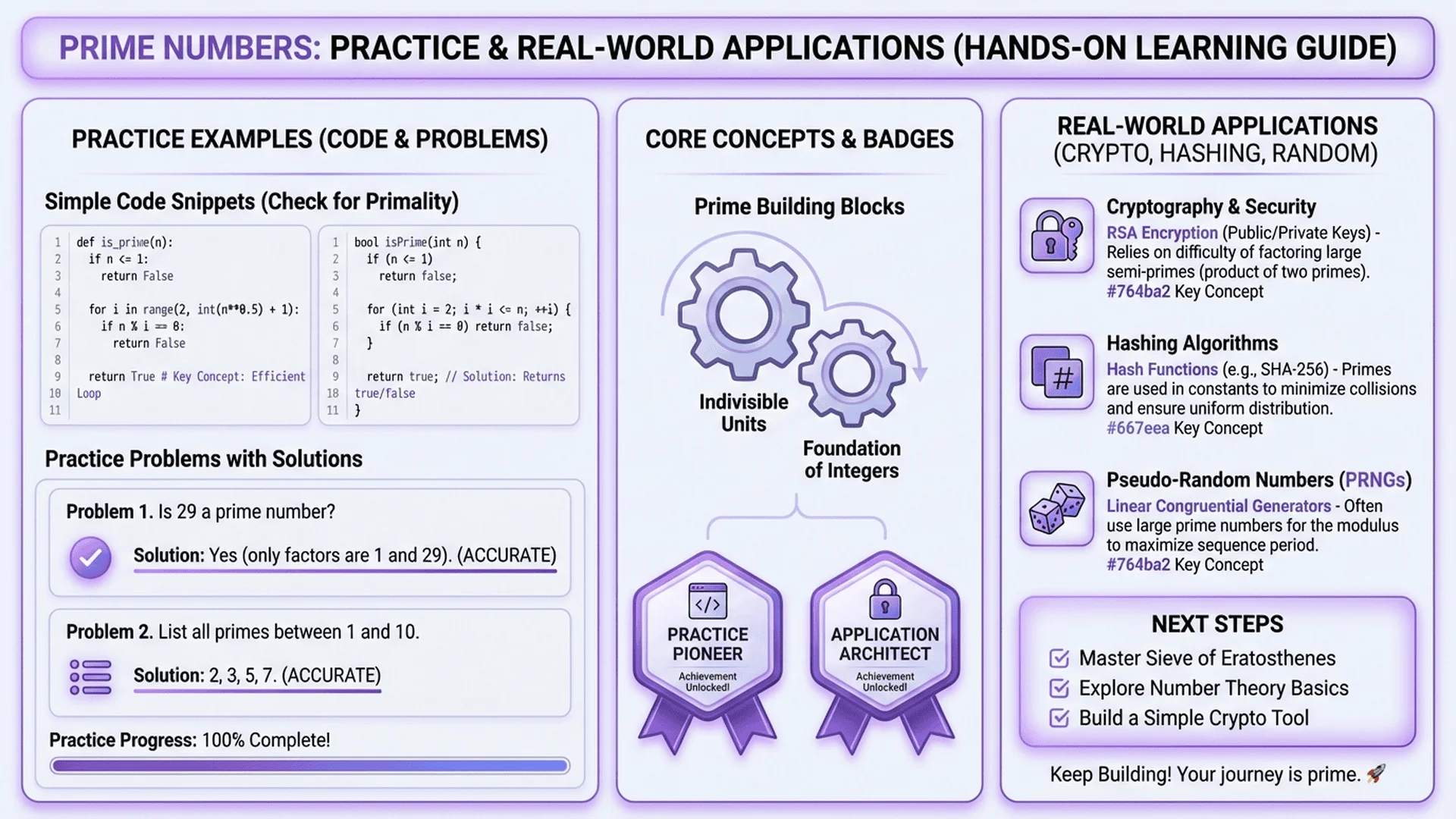
Minutes 7-8: Simple Code (Copy & Paste Ready)
Want to code your own prime checker? Here's the simplest version in Python:
Beginner-Friendly Python Code
def is_prime(n):
"""Check if n is a prime number."""
# Handle special cases
if n <= 1:
return False # 0, 1, and negatives are not prime
if n == 2:
return True # 2 is the only even prime
if n % 2 == 0:
return False # Other even numbers are not prime
# Check odd divisors up to √n
i = 3
while i * i <= n:
if n % i == 0:
return False
i += 2 # Skip even numbers
return True
# Test it yourself!
test_numbers = [2, 15, 17, 20, 29, 100, 97]
for num in test_numbers:
result = "prime" if is_prime(num) else "not prime"
print(f"{num} is {result}")
Output:
2 is prime
15 is not prime
17 is prime
20 is not prime
29 is prime
100 is not prime
97 is prime
How It Works (Line by Line)
- Lines 3-5: Reject numbers ≤ 1 (not prime by definition)
- Lines 6-7: Return True for 2 (the only even prime)
- Lines 8-9: Reject other even numbers (divisible by 2)
- Lines 11-16: Test odd divisors (3, 5, 7...) up to √n
- Line 18: If no divisors found, it's prime!
Try it yourself:
1. Copy the code above
2. Paste into Python Online Compiler
3. Click "Run"
4. Change the test_numbers list to try different numbers!
Want to learn more coding? Check out our Python Prime Number Check Tutorial for a deep dive into optimizing prime checking algorithms, or explore our complete Python Programming Tools collection for interactive practice!
Minute 9: Common Mistakes to Avoid
Mistake #1: Thinking 1 is Prime ❌
Why it's wrong: By mathematical definition, primes must have exactly two distinct divisors. 1 only has one divisor (itself).
Correct: 1 is neither prime nor composite.
Mistake #2: Forgetting 2 is Prime ❌
Why it's confusing: 2 is the only even prime number. Every other even number is divisible by 2, so they're not prime.
Remember: 2 is special—the smallest and only even prime!
Mistake #3: Testing All Numbers Up to n ❌
Why it's inefficient: You only need to test up to √n.
Example: To check if 100 is prime, test divisors 2-10, not 2-99!
Mistake #4: Not Handling Negative Numbers ❌
Why it matters: Prime numbers are defined only for positive integers greater than 1.
Correct approach: Always check if n <= 1 first!
Mistake #5: Trusting Unreliable Tools ❌
The problem: Some online calculators give wrong answers for large numbers or store your data.
Solution: Use verified tools like Tool Master's Prime Checker that process everything locally and show their methodology. For extremely large numbers (cryptographic primes), see our Large Prime Number Detection Guide.
Call-to-Action: Ready to Master Prime Checking?
| 🎯 Your Next Steps | 🔗 Resources |
|---|---|
| Check any number instantly | Free Prime Number Checker Tool → |
| Explore all math tools | Math Tools Collection → |
| Learn advanced algorithms | Prime Algorithms Comparison Guide → |
Bookmark this page and share it with classmates who struggle with prime numbers!
Minute 10: Practice Challenge
Test your new skills! Which of these numbers are prime? (No calculators!)
- 11 – Prime or not?
- 25 – Prime or not?
- 31 – Prime or not?
- 49 – Prime or not?
- 53 – Prime or not?
Answers:
1. ✅ Prime (divisors: 1, 11)
2. ❌ Not prime (divisible by 5: 25 = 5 × 5)
3. ✅ Prime (no divisors between 2 and √31 ≈ 5.6)
4. ❌ Not prime (divisible by 7: 49 = 7 × 7)
5. ✅ Prime (no divisors between 2 and √53 ≈ 7.3)
How did you do?
- 5/5 correct: You're a prime master! 🎓 Ready for advanced topics? Explore our Prime Algorithms Comparison
- 3-4 correct: Great job! Keep practicing with our interactive prime checker 👍
- 0-2 correct: Review the √n rule and try our online tool for instant feedback
Quick Reference Cheat Sheet
Print this or save it to your phone!
| Concept | What to Remember |
|---|---|
| Definition | Prime = only divisible by 1 and itself |
| Smallest prime | 2 (the only even prime) |
| Special cases | 0, 1, and negatives are NOT prime |
| Manual check | Test divisors from 2 to √n |
| First 10 primes | 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29 |
| Quick trick | Even numbers (except 2) are never prime |
| Fastest method | Use Tool Master's checker |
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Why isn't 1 considered a prime number?
Answer: Mathematicians define prime numbers as having exactly two distinct positive divisors: 1 and the number itself. Since 1 only has one divisor (itself), it doesn't meet the definition. This convention also makes mathematical theorems (like the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic) work correctly.
Key point: 1 is special—it's neither prime nor composite.
2. What's the easiest way to check if a large number is prime?
Answer: For numbers larger than 100, use a reliable online tool like Tool Master's Prime Checker. It can handle numbers up to 10^15 instantly. Manual checking becomes impractical for large numbers—for example, checking if 1,000,003 is prime would require testing hundreds of divisors by hand!
Pro tip: For numbers beyond 10^15, see our guide on Large Prime Number Detection, which covers cryptographic-scale primes and advanced algorithms like Miller-Rabin.
3. How do I remember which small numbers are prime?
Answer: Use the "2, 3, 5, 7 rule" for single digits:
- Memorize: 2, 3, 5, 7 are the only single-digit primes
- Not prime: 4 (2×2), 6 (2×3), 8 (2×4), 9 (3×3)
For 10-30, memorize: 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29
Trick: All primes > 3 end in 1, 3, 7, or 9 (never 0, 2, 4, 5, 6, 8).
4. Can negative numbers be prime?
Answer: No. Prime numbers are defined only for positive integers greater than 1. So -7, -3, 0, and 1 are all NOT prime.
Why: The concept of "divisibility" used in the prime definition applies to the natural counting numbers (1, 2, 3, 4...).
5. Is there a pattern to prime numbers?
Answer: Unfortunately, no simple pattern exists! Mathematicians have searched for centuries, but primes appear somewhat randomly. However, we know:
- Primes become less frequent as numbers get larger
- Gaps between primes can be arbitrarily large
- Approximately n/ln(n) primes exist below n (Prime Number Theorem)
Fun fact: Finding patterns in primes is one of the biggest unsolved problems in mathematics!
What You've Learned in 10 Minutes
Congratulations! You now know:
✅ The definition of prime numbers
✅ Manual checking method using the √n rule
✅ How to code a simple prime checker in Python
✅ The fastest online tools for instant results
✅ Common mistakes to avoid
✅ Practice problems to test your skills
Next steps:
- 🔖 Bookmark Tool Master's Prime Checker for homework help
- 📚 Learn more: Read our Prime Number Check Complete Guide for advanced techniques
- 💻 Practice coding: Try our Python Prime Number Tutorial for deeper coding knowledge
- 🎓 Explore math: Check out our full Math Tools Collection
- 🔍 Compare algorithms: See our Prime Algorithms Comparison to understand which method is fastest
- 📖 Discover history: Learn about Prime Numbers in History and Applications
Remember: Prime checking is a fundamental skill in math and computer science. The more you practice, the easier it becomes!
Practice Answers
From "Minutes 3-4: Quick Practice":
-
Is 17 prime?
✅ YES – √17 ≈ 4.1, so test 2, 3, 4. None divide evenly → 17 is prime! -
Is 21 prime?
❌ NO – 21 ÷ 3 = 7 (evenly divisible) → 21 = 3 × 7 is composite. -
Is 37 prime?
✅ YES – √37 ≈ 6.1, test 2-6. None divide evenly → 37 is prime!
Ready to check your homework answers in seconds? Try our Prime Number Checker now – it's free, fast, and works on any device! Want to explore different prime checking methods? Check out our Best Online Prime Checkers Review to see how different tools compare. 🚀
Last updated: January 2025 | Reading time: 7 minutes | Difficulty: Beginner