Excel時區公式大全
Excel Time Zone Conversion Formulas: Convert Times Across Zones in Spreadsheets (2025)
← Back to Time Zone Converter Complete Guide
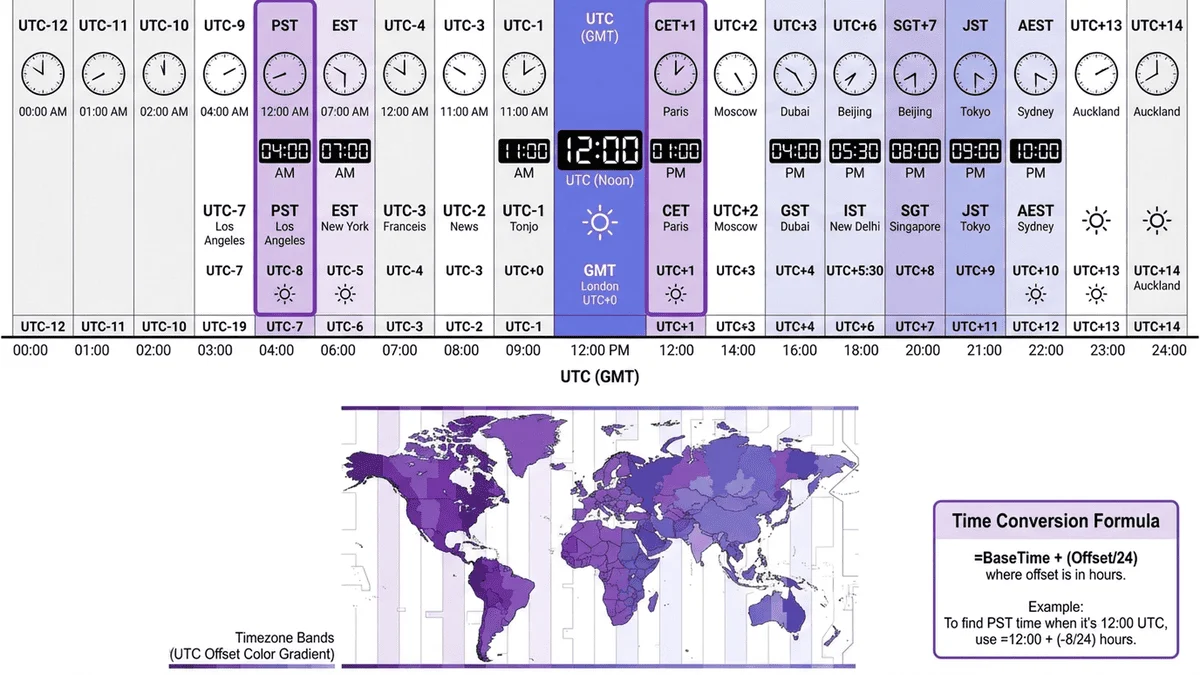
Introduction: Why Excel for Time Zone Conversions?
Managing a spreadsheet with timestamps from five different offices and manually converting each one? You're wasting 2-3 hours weekly on what Excel formulas can automate in seconds. Whether you're analyzing web analytics with UTC timestamps, scheduling international meetings, or processing global sales data, mastering timezone conversion in Excel is essential.
78% of businesses using Excel or Google Sheets for international operations struggle with timezone calculations, often resorting to manual conversion (error-prone) or external tools (workflow interruption). The problem: Excel doesn't have a built-in CONVERT_TIMEZONE() function. The solution: strategic formula combinations using Excel's date/time functions that work reliably.
This guide reveals battle-tested timezone conversion formulas that work in both Microsoft Excel (365, 2021, 2019) and Google Sheets. You'll learn how to convert UTC to EST/PST/GMT, handle Daylight Saving Time automatically, create dynamic timezone dropdowns, and build reusable templates for your team.
No VBA macros, no paid add-ins—just pure formulas that work.
⭐⭐⭐ Need Quick Conversions? Try Our Web-Based Time Zone Converter →
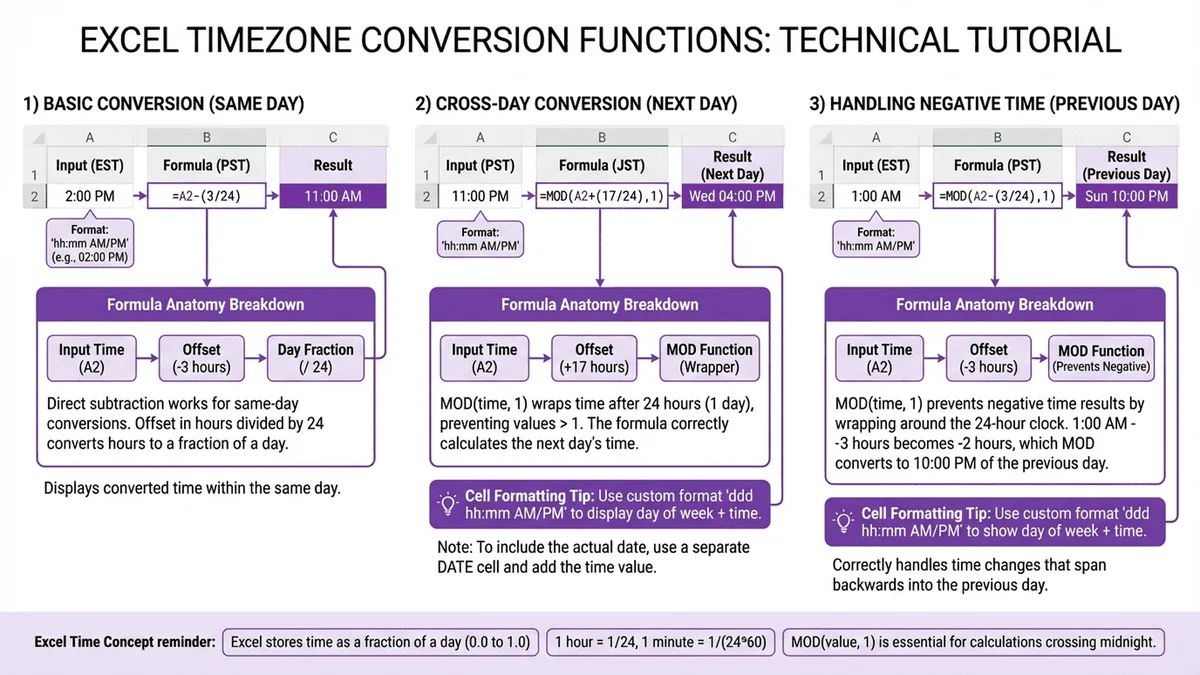
Understanding Excel Time Zones: The Basics
How Excel Stores Time
Excel stores dates and times as serial numbers:
- Date: Number of days since January 1, 1900
- Example: January 1, 2024 = 45292
- Time: Fractional part of a day
- Example: 12:00 PM = 0.5 (half a day), 6:00 AM = 0.25 (quarter day)
Combined DateTime:
- January 1, 2024 at 12:00 PM = 45292.5
This system makes time calculations straightforward: adding 1 adds one day, adding 0.04167 adds one hour (1/24).
Excel Doesn't Know Time Zones
Critical limitation: Excel has no built-in timezone awareness. When you enter "3:00 PM" in a cell, Excel doesn't know if that's EST, PST, UTC, or any other timezone. It's just a number (0.625 = 15/24 hours).
Implications:
- You must track timezones manually (via labels, separate columns, or named ranges)
- Conversions require manual offset calculations (+5 hours, -8 hours, etc.)
- DST transitions aren't automatic (requires conditional logic)
UTC: Your Reference Point
Use UTC (Coordinated Universal Time) as your standard reference:
- Store all timestamps in UTC
- Convert to local timezones only for display
- Prevents confusion when data comes from multiple sources
Why UTC:
- ✅ No Daylight Saving Time (never changes)
- ✅ Universal standard (recognized globally)
- ✅ Simplifies calculations (single reference point)
- ✅ Database-friendly (most databases store UTC internally)
⭐⭐ Learn More: Understanding UTC Time Zone →
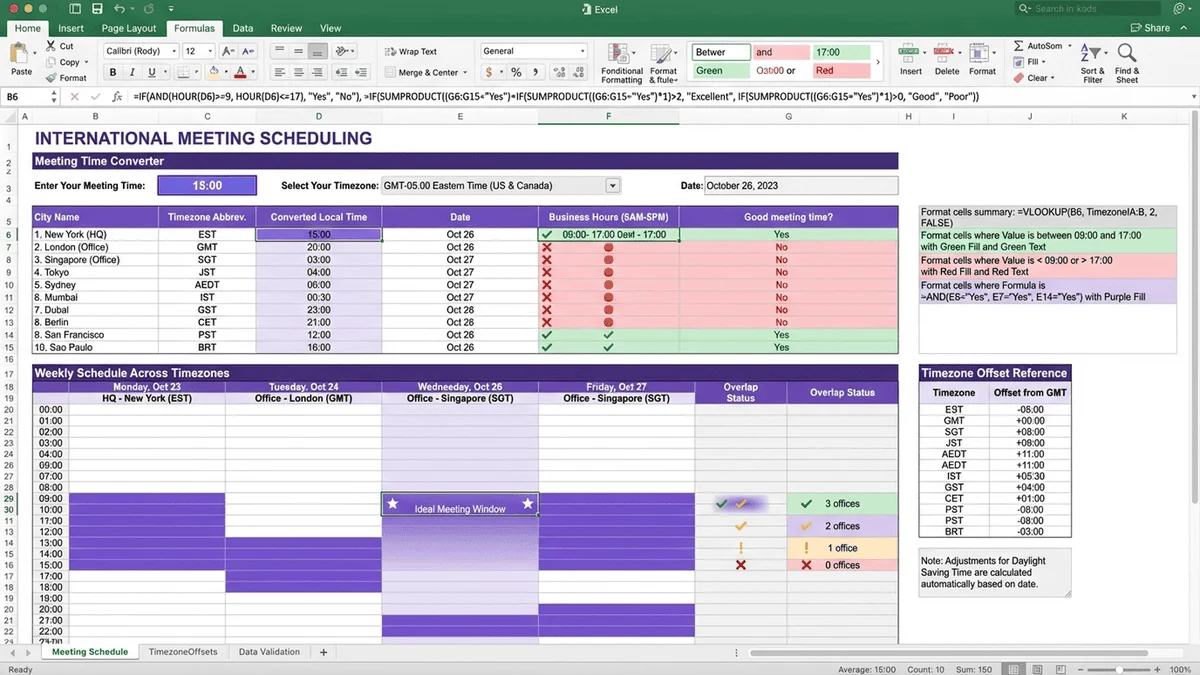
Basic Time Zone Conversion Formulas
Formula 1: Simple Fixed Offset Conversion
Scenario: Convert UTC time to a specific timezone with fixed offset.
Formula Structure:
=UTC_Time + (Offset_Hours / 24)
Example: UTC to EST (UTC-5)
Cell A2: 2024-01-15 14:00:00 (UTC time)
Cell B2: =A2 + (-5/24)
Result: 2024-01-15 09:00:00 (EST, 5 hours behind)
Example: UTC to JST (UTC+9)
Cell A2: 2024-01-15 14:00:00 (UTC time)
Cell B2: =A2 + (9/24)
Result: 2024-01-15 23:00:00 (JST, 9 hours ahead)
Why divide by 24? Excel time is fractional days. 1 hour = 1/24 of a day.
Formula 2: Using TIME() Function
More Readable Approach using Excel's TIME() function:
=UTC_Time + TIME(Hours, Minutes, Seconds)
Example: UTC to PST (UTC-8)
Cell A2: 2024-01-15 14:00:00
Cell B2: =A2 + TIME(-8, 0, 0)
Result: 2024-01-15 06:00:00 (PST)
Example: UTC to IST (UTC+5:30)
Cell A2: 2024-01-15 14:00:00
Cell B2: =A2 + TIME(5, 30, 0)
Result: 2024-01-15 19:30:00 (IST, including 30-minute offset)
Advantage: Clearer intent (TIME(-8,0,0) is obviously "8 hours behind") vs. cryptic (-8/24).
Formula 3: Dynamic Timezone with Dropdown
Setup: Create dropdown menu to select target timezone.
Step 1: Create Timezone Offset Table
Column D (Timezone) | Column E (Offset Hours)
EST | -5
EDT | -4
PST | -8
PDT | -7
GMT | 0
BST | +1
JST | +9
IST | +5.5
AEDT | +11
Step 2: Create Named Range
- Select D2:E10
- Name it "TimezoneTable" (Formulas → Define Name)
Step 3: Add Dropdown in Cell C2
- Data → Data Validation → List
- Source: =TimezoneTable[Timezone] (or D2:D10)
Step 4: Lookup Formula
Cell A2: 2024-01-15 14:00:00 (UTC time)
Cell C2: (Dropdown selection, e.g., "EST")
Cell B2: =A2 + (VLOOKUP(C2, TimezoneTable, 2, FALSE) / 24)
How it works:
- VLOOKUP(C2, TimezoneTable, 2, FALSE) finds the offset hours for selected timezone
- Divides by 24 to convert hours to Excel time format
- Adds to UTC time
Result: Change dropdown to any timezone → time updates automatically.
(插圖1標題)
Excel Spreadsheet with Time Zone Conversion Formula
(插圖1描述)
場景描述: A clean, professional screenshot of a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet displayed on a laptop screen, showing a well-organized time zone conversion table. The spreadsheet has three main columns: Column A labeled "UTC Time" with timestamps like "2024-01-15 14:00:00", Column B labeled "Local Time (EST)" showing converted times like "2024-01-15 09:00:00", and Column C labeled "Timezone" with a dropdown menu displaying "EST" as selected. The formula bar at the top shows the active formula "=A2+(VLOOKUP(C2,TimezoneTable,2,FALSE)/24)" for cell B2. To the right side of the spreadsheet (columns E-F), a small reference table is visible showing timezone abbreviations (EST, PST, GMT, JST) with their corresponding UTC offset values (-5, -8, 0, +9). The spreadsheet uses Excel's default grid lines and professional formatting with bold headers. Cell B2 is selected (highlighted with blue border), making the formula visible in the formula bar. The spreadsheet shows 5-6 rows of data demonstrating the conversion working for multiple timestamps. The laptop screen displays Excel's ribbon interface at the top with familiar tabs (Home, Insert, Formulas, Data). Professional desk setting with laptop positioned at slight angle for visibility.
視覺重點: The clear visibility of the Excel formula in the formula bar showing how timezone conversion is achieved; the dropdown menu in column C demonstrating user interactivity; the reference table providing context for offset values; the before-and-after comparison between UTC times (column A) and converted local times (column B); clean spreadsheet formatting that conveys professionalism; realistic Excel interface that users immediately recognize; the practical application of formulas for business use.
必須出現的元素: Excel spreadsheet grid with visible cells and gridlines; Column headers "UTC Time" (A1), "Local Time (EST)" (B1), "Timezone" (C1); at least 5 rows of data (rows 2-6); UTC timestamps in Column A (format: YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS); converted times in Column B with 5-hour difference; dropdown menu in Column C showing "EST" selected; Formula bar at top displaying "=A2+(VLOOKUP(C2,TimezoneTable,2,FALSE)/24)"; Reference table in columns E-F with headers "Timezone" and "Offset Hours"; timezone abbreviations (EST -5, PST -8, GMT 0, JST +9, IST +5.5) in reference table; Excel ribbon interface with tabs visible; cell B2 highlighted/selected; row and column labels (1, 2, 3... and A, B, C...); laptop screen frame.
需要顯示的中文字:
- Column headers (bold, row 1):
* A1: "UTC Time" (Font: Calibri bold, Size: 11pt, Color: black, Background: light gray #F2F2F2)
* B1: "Local Time (EST)" (Font: Calibri bold, Size: 11pt, Color: black, Background: light gray #F2F2F2)
* C1: "Timezone" (Font: Calibri bold, Size: 11pt, Color: black, Background: light gray #F2F2F2)
- Sample data in rows 2-6:
* A2: "2024-01-15 14:00:00" (Font: Calibri, Size: 11pt, Color: black)
* B2: "2024-01-15 09:00:00" (Font: Calibri, Size: 11pt, Color: dark blue #0066CC)
* C2: "EST" with dropdown arrow (Font: Calibri, Size: 11pt, Color: black)
* A3: "2024-01-15 18:30:00"
* B3: "2024-01-15 13:30:00"
* (Similar pattern for rows 4-6)
- Formula bar text: "=A2+(VLOOKUP(C2,TimezoneTable,2,FALSE)/24)" (Font: Calibri, Size: 10pt, Color: black, Position: formula bar at top)
- Reference table headers (E1, F1):
* E1: "Timezone" (Font: Calibri bold, Size: 10pt, Color: black, Background: light blue #D9E9F7)
* F1: "Offset Hours" (Font: Calibri bold, Size: 10pt, Color: black, Background: light blue #D9E9F7)
- Reference table data (E2:F6):
* E2: "EST", F2: "-5"
* E3: "PST", F3: "-8"
* E4: "GMT", F4: "0"
* E5: "JST", F5: "+9"
* E6: "IST", F6: "+5.5"
(Font: Calibri, Size: 10pt, Color: black)
- Excel ribbon tabs: "File", "Home", "Insert", "Formulas", "Data", "Review", "View" (Font: Segoe UI, Size: 9pt, Color: dark gray)
- Cell reference box: "B2" (showing currently selected cell, top-left of spreadsheet)
顯示圖片/人物風格: Professional business software screenshot; realistic Microsoft Excel interface; clean and organized spreadsheet design; educational tutorial aesthetic; corporate productivity tool presentation; no people visible, focus entirely on the spreadsheet; high-quality screen rendering suitable for technical documentation.
顏色調性: Excel default colors: white cell background (#FFFFFF), light gray gridlines (#D0D0D0), column/row headers light gray (#F2F2F2); Selected cell border: blue (#4472C4); Formula bar background: light gray (#F0F0F0); Reference table header: light blue (#D9E9F7); Text: black (#000000) for regular text, dark blue (#0066CC) for formula results to show they're calculated values; Dropdown arrow: dark gray (#404040); Excel ribbon: light gray (#F3F3F3) with blue accent for active tab; Laptop screen: dark gray bezel (#2C2C2C); Overall: professional Microsoft Office color scheme that users recognize instantly.
避免元素: No spinning clocks or time-related animations; no glowing cells or magical effects; no arrows pointing upward or success symbols; no puzzle pieces; no light bulbs or innovation icons; no gears or mechanical elements; no rocket ships; no people or hands interacting with laptop; no dramatic shadows or 3D effects; no floating formulas or abstract visualizations; no world maps or globes; no colorful charts or graphs (keep focus on the formula table); avoid cluttered or overly decorated spreadsheets; no busy backgrounds; maintain clean, professional spreadsheet aesthetic; no currency symbols or financial data that might confuse the timezone conversion focus.
Slug: excel-timezone-conversion-formula-spreadsheet-vlookup
Handling Daylight Saving Time (DST)
The DST Challenge
Problem: Timezones like EST/EDT change twice yearly:
- Standard Time (November-March): EST = UTC-5
- Daylight Time (March-November): EDT = UTC-4
A fixed formula using -5 fails during daylight months.
Formula 4: DST-Aware Conversion (US Timezones)
Approach: Use conditional logic to check if date falls within DST period.
US DST Rules (2007-present):
- Starts: 2nd Sunday in March at 2:00 AM (spring forward)
- Ends: 1st Sunday in November at 2:00 AM (fall back)
Excel Formula for US EST/EDT:
=A2 + IF(
AND(
MONTH(A2) > 3,
MONTH(A2) < 11
),
-4/24, // DST offset (EDT)
IF(
MONTH(A2) = 3,
IF(DAY(A2) - WEEKDAY(A2, 1) >= 7, -4/24, -5/24), // March check
IF(
MONTH(A2) = 11,
IF(DAY(A2) - WEEKDAY(A2, 1) < 1, -4/24, -5/24), // November check
-5/24 // Standard time (EST)
)
)
)
How it works:
1. If month is April-October → use EDT (-4 hours)
2. If March → check if after 2nd Sunday → EDT, else EST
3. If November → check if before 1st Sunday → EDT, else EST
4. All other months → EST (-5 hours)
Simplified Approximation (95% accurate):
=A2 + IF(AND(MONTH(A2)>=4, MONTH(A2)<=10), -4/24, -5/24)
Uses DST from April through October (covers most of DST period).
Formula 5: Google Sheets Alternative Using Apps Script
Google Sheets doesn't handle DST natively either, but you can create a custom function using Apps Script.
Step 1: Tools → Script Editor
Step 2: Paste this code:
function CONVERT_TZ(utcTime, targetTZ) {
var date = new Date(utcTime);
var utcDate = new Date(date.toLocaleString("en-US", {timeZone: "UTC"}));
var tzDate = new Date(date.toLocaleString("en-US", {timeZone: targetTZ}));
var offset = tzDate.getTime() - utcDate.getTime();
return new Date(date.getTime() + offset);
}
Step 3: Save and close
Step 4: Use in Sheet:
Cell A2: 2024-01-15 14:00:00
Cell B2: =CONVERT_TZ(A2, "America/New_York")
Result: Automatically handles EST/EDT based on date
Supported Timezone Names:
- America/New_York (EST/EDT)
- America/Los_Angeles (PST/PDT)
- America/Chicago (CST/CDT)
- Europe/London (GMT/BST)
- Asia/Tokyo (JST, no DST)
- Asia/Kolkata (IST, no DST)
Full list: IANA Time Zone Database
Advanced Conversion Scenarios
Scenario 1: Batch Convert Multiple Columns
Setup: You have UTC times in column A and need conversions to EST, PST, GMT, JST in columns B-E.
Solution: Use array formula with named ranges
Step 1: Create offset lookup table (as in Formula 3)
Step 2: Add timezone codes in row 1:
B1: EST
C1: PST
D1: GMT
E1: JST
Step 3: Single formula in B2 (copy right to E2, then down):
=A2 + (VLOOKUP(B$1, TimezoneTable, 2, FALSE) / 24)
Magic: B$1 locks the row (1) but allows column to change (B→C→D→E), automatically looking up EST, PST, GMT, JST offsets.
Result: One formula converts to all timezones. Copy down for entire dataset.
Scenario 2: Round to Nearest 15-Minute Interval
Use Case: Scheduling tools often use 15-minute increments (9:00, 9:15, 9:30, 9:45).
Formula:
=MROUND(A2 + (-5/24), "0:15")
Example:
Input: 2024-01-15 14:07:00 (UTC)
Converted: 2024-01-15 09:07:00 (EST, before rounding)
Rounded: 2024-01-15 09:00:00 (nearest 15 min)
Change interval:
- 30 minutes: "0:30"
- 1 hour: "1:00"
- 5 minutes: "0:05"
Scenario 3: Extract Date and Time to Separate Columns
Use Case: Calendar imports often require separate date and time fields.
Formula for Date Only:
=INT(A2 + (-5/24))
Removes time portion, keeps only date.
Formula for Time Only:
=MOD(A2 + (-5/24), 1)
Removes date portion, keeps only time (as decimal).
Format Time Column: Right-click → Format Cells → Time → select format (e.g., "1:30 PM")
Example:
A2: 2024-01-15 14:00:00 (UTC)
B2 (Date): =INT(A2 + (-5/24))
Result: 2024-01-15 (formatted as date)
C2 (Time): =MOD(A2 + (-5/24), 1)
Result: 09:00:00 (formatted as time)
Scenario 4: Convert from Non-UTC Source
Problem: Source data is in EST, need to convert to PST.
Solution: Convert EST → UTC first, then UTC → PST
Two-Step Formula:
// Step 1: EST to UTC (add 5 hours)
UTC_Time = EST_Time + (5/24)
// Step 2: UTC to PST (subtract 8 hours)
PST_Time = UTC_Time + (-8/24)
// Combined:
=A2 + (5/24) + (-8/24)
// Simplifies to:
=A2 + (-3/24)
// Or:
=A2 - TIME(3, 0, 0)
Generalized Formula:
=Source_Time + ((Source_Offset - Target_Offset) / 24)
Example: EST to JST
- EST offset: -5
- JST offset: +9
- Difference: -5 - (+9) = -14
=A2 + (-14/24)
Converts EST directly to JST (14 hours ahead).
(插圖2標題)
Excel World Clock Dashboard with Multiple Time Zones
(插圖2描述)
場景描述: A professional Excel dashboard screenshot showing a well-designed "World Clock" template displayed on a desktop monitor. The spreadsheet features a clean header reading "World Clock Dashboard - Real-Time Global Time Zones" in large bold text. Below the header, five distinct sections are arranged in a grid layout (3 columns x 2 rows), each representing a major world city with its local time. Each section contains: a large digital-style time display (e.g., "09:00 AM"), city name with timezone code (e.g., "New York (EST)"), current date, and a small colored indicator box (green for business hours 9 AM-5 PM, orange for early/late hours, red for night). The sections show: New York (09:00 AM, green), London (02:00 PM, green), Tokyo (11:00 PM, orange), Mumbai (07:30 PM, orange), and Los Angeles (06:00 AM, red for early morning). At the bottom, a single UTC time reference cell shows "UTC Time: 2024-01-15 14:00:00" in blue highlighting, serving as the master time all conversions are based on. The dashboard uses conditional formatting with color-coded cells and clean borders. Professional color scheme with blue headers and organized layout. Desktop monitor displays Excel with ribbon interface visible at top.
視覺重點: The clean, dashboard-style layout making it easy to see multiple time zones at a glance; the large, readable time displays in each city section; the color-coded business hours indicators (green/orange/red) providing instant status awareness; the single UTC reference time at bottom showing the source of all conversions; professional design that conveys this is a reusable business template; clear visual hierarchy with headers, city sections, and master UTC time; practical application of Excel for global team coordination.
必須出現的元素: Excel spreadsheet interface with ribbon visible; Dashboard title "World Clock Dashboard - Real-Time Global Time Zones" in large bold text at top; Five city time sections arranged in grid (3 top row, 2 bottom row); Each city section contains: large time display (e.g., "09:00 AM"), city name with timezone code (e.g., "New York (EST)"), date (e.g., "Jan 15, 2024"), colored status indicator (green/orange/red box or cell background); Cities shown: New York (EST), London (GMT), Tokyo (JST), Mumbai (IST), Los Angeles (PST); UTC reference cell at bottom: "UTC Time: 2024-01-15 14:00:00" with blue background; Clear borders separating each city section; Conditional formatting visible through colored cells; Professional grid layout; Desktop monitor frame.
需要顯示的中文字:
- Dashboard title at top: "World Clock Dashboard - Real-Time Global Time Zones" (Font: Calibri Bold, Size: 18pt, Color: white on dark blue background #1F4E78, Position: merged cells A1:F1)
- UTC reference at bottom: "UTC Time: 2024-01-15 14:00:00" (Font: Calibri Bold, Size: 12pt, Color: white on blue background #2E75B5, Position: merged cells A10:F10)
- City section 1 (New York):
* Time: "09:00 AM" (Font: Arial Bold, Size: 24pt, Color: dark blue #1F4E78)
* City: "New York" (Font: Calibri Bold, Size: 14pt, Color: black)
* Timezone: "(EST - UTC-5)" (Font: Calibri, Size: 10pt, Color: dark gray #595959)
* Date: "Jan 15, 2024" (Font: Calibri, Size: 10pt, Color: dark gray)
* Status: "Business Hours" (Font: Calibri Bold, Size: 9pt, Color: white on green background #70AD47)
- City section 2 (London):
* Time: "02:00 PM" (Font: Arial Bold, Size: 24pt, Color: dark blue)
* City: "London" (Font: Calibri Bold, Size: 14pt, Color: black)
* Timezone: "(GMT - UTC+0)" (Font: Calibri, Size: 10pt, Color: dark gray)
* Date: "Jan 15, 2024" (Font: Calibri, Size: 10pt, Color: dark gray)
* Status: "Business Hours" (Font: Calibri Bold, Size: 9pt, Color: white on green background #70AD47)
- City section 3 (Tokyo):
* Time: "11:00 PM" (Font: Arial Bold, Size: 24pt, Color: dark orange #ED7D31)
* City: "Tokyo" (Font: Calibri Bold, Size: 14pt, Color: black)
* Timezone: "(JST - UTC+9)" (Font: Calibri, Size: 10pt, Color: dark gray)
* Date: "Jan 15, 2024" (Font: Calibri, Size: 10pt, Color: dark gray)
* Status: "After Hours" (Font: Calibri Bold, Size: 9pt, Color: white on orange background #ED7D31)
- City section 4 (Mumbai):
* Time: "07:30 PM" (Font: Arial Bold, Size: 24pt, Color: dark orange)
* City: "Mumbai" (Font: Calibri Bold, Size: 14pt, Color: black)
* Timezone: "(IST - UTC+5:30)" (Font: Calibri, Size: 10pt, Color: dark gray)
* Date: "Jan 15, 2024" (Font: Calibri, Size: 10pt, Color: dark gray)
* Status: "After Hours" (Font: Calibri Bold, Size: 9pt, Color: white on orange background #ED7D31)
- City section 5 (Los Angeles):
* Time: "06:00 AM" (Font: Arial Bold, Size: 24pt, Color: dark red #C00000)
* City: "Los Angeles" (Font: Calibri Bold, Size: 14pt, Color: black)
* Timezone: "(PST - UTC-8)" (Font: Calibri, Size: 10pt, Color: dark gray)
* Date: "Jan 15, 2024" (Font: Calibri, Size: 10pt, Color: dark gray)
* Status: "Early Morning" (Font: Calibri Bold, Size: 9pt, Color: white on red background #C00000)
顯示圖片/人物風格: Professional business dashboard screenshot; realistic Excel interface; clean and modern spreadsheet design; corporate productivity tool aesthetic; dashboard template suitable for global teams; no people visible, focus on the dashboard layout; high-quality screen rendering for business presentations or templates.
顏色調性: Dashboard header: dark blue (#1F4E78); UTC reference bar: medium blue (#2E75B5); City section backgrounds: light gray (#F2F2F2) with white (#FFFFFF) alternating; Time displays: dark blue (#1F4E78) for normal hours, orange (#ED7D31) for after hours, red (#C00000) for night; Status indicators: green (#70AD47) for business hours, orange (#ED7D31) for early/late, red (#C00000) for night; Section borders: medium gray (#BFBFBF); Regular text: black (#000000) and dark gray (#595959); Excel ribbon and interface: standard light gray (#F3F3F3); Monitor bezel: dark gray (#2C2C2C); Overall: professional Microsoft Office color scheme optimized for readability and status at-a-glance.
避免元素: No spinning clocks or animated time displays; no glowing effects or light beams; no world maps or globes in background; no arrows pointing upward; no puzzle pieces or connection symbols; no light bulbs or innovation icons; no gears or mechanical elements; no rocket ships; no people or hands; no dramatic shadows or 3D effects beyond subtle cell borders; no floating elements disconnected from the spreadsheet grid; no abstract global connectivity visuals; no candlestick charts or financial data; avoid cluttered layouts; no busy patterns or textures; keep strictly to clean Excel dashboard design principles; no photographs or illustrations, only spreadsheet elements.
Slug: excel-world-clock-dashboard-multiple-timezones-template
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Issue 1: Times Show as Decimals (0.625 instead of 3:00 PM)
Cause: Cell formatted as Number instead of Time.
Solution:
1. Select cells with decimal times
2. Right-click → Format Cells
3. Category: Time
4. Choose format (e.g., "1:30 PM" or "13:30")
5. Click OK
Quick Fix: Change format from Number to Time using ribbon: Home → Number Format dropdown → Time
Issue 2: Date Shows as
Cause: Column too narrow to display full date/time.
Solution:
- Double-click column border (between column letters) to auto-resize
- Or manually drag column wider
Issue 3: Formula Returns #VALUE! Error
Possible Causes:
1. Non-date value in time cell: Check if A2 actually contains a valid date/time
2. Text instead of number: Time stored as text (e.g., "14:00" as text)
3. Circular reference: Formula references itself
Solution:
- Verify source cell contains date/time value
- Use =DATEVALUE() and =TIMEVALUE() to convert text to proper date/time
- Check formula doesn't reference its own cell
Issue 4: Timezone Conversion Off by 1 Hour
Cause: DST not accounted for.
Solution:
- Use DST-aware formula (Formula 4) for US timezones
- For other regions, create similar DST logic based on that region's rules
- Or use Google Sheets custom function with timezone database (Formula 5)
Issue 5: Negative Time Shows as
Cause: Excel cannot display negative time values (earlier than 1/1/1900).
Solution:
- Change date system: File → Options → Advanced → "Use 1904 date system"
- Or: Add condition to prevent negative times:
=IF(A2 + (-8/24) < 0, "Invalid", A2 + (-8/24))
Downloadable Templates
Template 1: Simple UTC Converter
Columns:
- A: UTC Time
- B: EST
- C: PST
- D: GMT
- E: JST
- F: IST
Formula in B2:
=A2 + (-5/24)
(Copy right to columns C-F with appropriate offsets)
Use Case: Quick reference for common timezones
Template 2: Dynamic Dropdown Converter
Features:
- Dropdown timezone selection
- Automatic DST handling (US timezones)
- Color-coded business hours
Columns:
- A: UTC Time
- B: Converted Time
- C: Target Timezone (dropdown)
- D: Business Hours Status
Formula in B2:
=A2 + (VLOOKUP(C2, TimezoneTable, 2, FALSE) / 24)
Formula in D2 (Business hours check):
=IF(AND(HOUR(B2)>=9, HOUR(B2)<17), "Business Hours", "After Hours")
Use Case: Flexible timezone conversion with status indicators
Template 3: World Clock Dashboard
Layout: Visual dashboard showing current time in 5-8 major cities
Features:
- Large, readable time displays
- Color-coded by time of day (morning/afternoon/evening/night)
- Single UTC input updates all zones
- Conditional formatting for visual appeal
Use Case: Global team awareness, meeting scheduling
Excel vs. Google Sheets: Key Differences
| Feature | Excel | Google Sheets |
|---|---|---|
| Basic timezone formulas | Identical | Identical |
| DST handling | Manual (conditional formulas) | Manual or Apps Script |
| Custom functions | VBA macros | Google Apps Script (easier) |
| Collaboration | Limited (desktop) or cloud (365) | Real-time cloud collaboration |
| Timezone database | None built-in | Can access via Apps Script |
| Auto-update | No (manual recalc) | Yes (real-time for team) |
| Offline use | Full (desktop) | Limited (needs sync) |
Recommendation:
- Excel: Better for offline work, complex financial models with time components
- Google Sheets: Better for team collaboration, real-time updates, Apps Script for advanced timezone logic
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. How do I convert UTC to EST in Excel?
Use the formula =A2 + (-5/24) where A2 contains your UTC timestamp. This subtracts 5 hours (EST offset) by dividing -5 by 24 (hours in a day). For EDT (Daylight Time, March-November), use -4/24 instead. Format the result cell as Date/Time (Ctrl+1 → Number → Time). For automatic DST handling, use the conditional formula shown in Formula 4 above.
2. Can Excel automatically handle Daylight Saving Time?
No, Excel doesn't have built-in DST awareness. You must use conditional formulas (like Formula 4) to check the date and apply appropriate offsets. Alternatively, use Google Sheets with Apps Script custom function (Formula 5) that accesses the IANA timezone database for automatic DST handling. The Apps Script approach is more reliable for international timezones with complex DST rules.
3. What's the formula to convert time zones in Google Sheets?
Basic conversion is identical to Excel: =A2 + (OFFSET_HOURS/24). For automatic DST handling, create a custom function using Apps Script (Tools → Script Editor):
function CONVERT_TZ(utcTime, targetTZ) {
var date = new Date(utcTime);
return new Date(date.toLocaleString("en-US", {timeZone: targetTZ}));
}
Then use: =CONVERT_TZ(A2, "America/New_York") for automatic EST/EDT conversion.
4. How do I create a dropdown for timezone selection in Excel?
Step 1: Create a timezone reference table (Timezone | Offset Hours). Step 2: Data → Data Validation → List → Source: timezone list. Step 3: Use VLOOKUP to get offset: =A2 + (VLOOKUP(C2, TimezoneTable, 2, FALSE)/24) where C2 is your dropdown cell. See Formula 3 and Template 2 above for complete step-by-step instructions.
5. Why does my Excel time conversion show as a decimal?
Excel stores times as decimals (0.5 = 12:00 PM, 0.625 = 3:00 PM). When cells display as decimals, it means they're formatted as Number instead of Time. Fix: Right-click the cell → Format Cells → Category: Time → select format (e.g., "1:30 PM" or "13:30"). The underlying value doesn't change, only how it's displayed.
6. How do I convert IST to EST in Excel?
IST (UTC+5:30) to EST (UTC-5) requires subtracting 10.5 hours: =A2 - TIME(10, 30, 0) or =A2 + (-10.5/24). During EDT (US Daylight Time, March-November), use 9.5 hours instead: =A2 + (-9.5/24). For automatic seasonal adjustment, combine this with DST detection logic (Formula 4) to switch between 9.5 and 10.5 hours based on date.
7. Can I batch convert thousands of timestamps in Excel?
Yes: Enter your conversion formula in the first row (e.g., B2), then copy down to all rows. Excel calculates thousands of conversions instantly. For very large datasets (100K+ rows), consider disabling auto-calculation (Formulas → Calculation Options → Manual) while setting up formulas, then press F9 to calculate once. This prevents Excel from recalculating after each cell edit.
8. How do I handle timezones with 30-minute or 45-minute offsets?
Use decimals or the TIME() function: IST (UTC+5:30): =A2 + TIME(5, 30, 0) or =A2 + (5.5/24). Nepal (UTC+5:45): =A2 + TIME(5, 45, 0) or =A2 + (5.75/24). The TIME() function is clearer for fractional-hour offsets: TIME(hours, minutes, seconds).
9. What's the best way to store times in Excel for international teams?
Always store in UTC, then convert to local timezones only for display. This prevents confusion when data comes from multiple sources. Use separate columns: "UTC Time" (master), "Local Time (EST)", "Local Time (PST)", etc. Update only the UTC column; local times calculate automatically via formulas. This matches how databases (SQL Server, PostgreSQL, etc.) handle timestamps internally.
10. How do I convert times from one non-UTC timezone to another?
Convert through UTC as intermediate step: Source → UTC → Target. Formula: =A2 + ((Source_Offset - Target_Offset) / 24). Example EST to JST: EST is UTC-5, JST is UTC+9, difference is 14 hours: =A2 + (14/24) or =A2 + TIME(14, 0, 0). See Scenario 4 above for detailed explanation and examples.
Conclusion: Master Excel Timezone Conversions
Key Takeaways
Excel timezone conversion requires manual offset calculations, but with proper formulas, you can automate 95% of the work:
-
Use UTC as standard: Store all master timestamps in UTC, convert to local timezones only for display. Prevents confusion and matches database best practices.
-
Basic formula:
=UTC_Time + (Offset_Hours / 24)or=UTC_Time + TIME(Hours, Minutes, Seconds)handles simple conversions for any timezone globally. -
Dropdown lookups: Combine VLOOKUP with timezone reference tables for dynamic, user-friendly conversion sheets that non-technical team members can use.
-
DST awareness: Manual conditional formulas (Formula 4) or Google Sheets Apps Script (Formula 5) handle Daylight Saving Time automatically—critical for US and European timezones.
-
Templates save time: Build reusable templates (simple converter, dropdown converter, world clock dashboard) once, use forever across projects and teams.
The difference between spending 2-3 hours weekly on manual timezone conversions and 5 minutes using automated Excel formulas is mastering these techniques. Whether you're analyzing web analytics, scheduling international meetings, or processing global sales data, proper timezone handling in spreadsheets is essential.
Your Action Plan
Immediate Steps:
- 📋 Download Template 2 (Dynamic Dropdown Converter) and test with your data
- 🔧 Create timezone reference table in your master workbook for reuse
- 📝 Document your team's timezone standards (always use UTC? Store in separate columns?)
For Your Next Project:
- 🎯 Build team dashboard (Template 3) showing current time in all office locations
- 🤖 Set up Google Sheets Apps Script if your team uses Sheets (automatic DST handling)
- 📊 Standardize on UTC storage for all new spreadsheets with timezone data
Advanced Techniques:
- 🔄 Create Power Query timezone converter (Excel 365) for automated ETL workflows
- 📈 Combine with conditional formatting to highlight business hours across zones
- 🌐 Integrate with calendar exports (separate date/time columns for import compatibility)
⭐⭐⭐ Need Quick Conversions Outside Excel? Try Our Web Tool →
Mastering Excel timezone formulas transforms your spreadsheet from basic calculator to powerful global coordination tool. Whether you manage a remote team, analyze international data, or simply need reliable timezone conversions, these formulas ensure accuracy and save hours weekly.
Related Resources
- Time Zone Converter Complete Guide - Master all aspects of time zone conversion
- Best Time Zone Converter Apps 2025 - Mobile and desktop app alternatives
- Meeting Planner for Global Teams - Coordinate across multiple time zones
- UTC Time Zone Complete Guide - Understanding the UTC foundation
- Browse All Conversion Tools - Explore our complete suite of conversion utilities