UTC時區完整指南
UTC Time Zone Complete Guide: Definition, Offset, and Conversion (2025)
Ever wondered why every digital system references "UTC"? From flight departure boards to software timestamps, UTC is the invisible backbone of our globally synchronized world. Yet most people don't truly understand what UTC means or how it differs from "regular" time zones. This confusion leads to miscalculated meeting times, missed deadlines, and scheduling chaos.
Here's the truth: UTC isn't just another time zone—it's the master reference that makes all other time zones possible. Understanding UTC is the key to mastering international coordination, whether you're a developer, business professional, or frequent traveler.
This comprehensive guide reveals everything about UTC: its history, how it works, offset calculations, and practical conversion methods you can use immediately.
← Back to Time Zone Converter Complete Guide
What is UTC Time Zone?
The Scientific Definition
UTC stands for "Coordinated Universal Time." It's the primary time standard by which the world regulates clocks and time.
Why the acronym doesn't match?
The abbreviation "UTC" is a compromise between English "CUT" (Coordinated Universal Time) and French "TUC" (Temps Universel Coordonné). International organizations chose the neutral "UTC" to avoid favoring either language.
Key characteristics:
1. Based on Atomic Time
- Maintained by atomic clocks (accurate to nanoseconds)
- Over 400 atomic clocks worldwide contribute to UTC
- International Bureau of Weights and Measures coordinates the system
2. Zero Point Reference
- UTC+0 located at the Prime Meridian (0° longitude)
- Passes through Greenwich, London (Royal Observatory)
- All other time zones calculated as offsets from UTC
3. Never Changes
- UTC doesn't observe Daylight Saving Time
- Constant reference point year-round
- Reliable for scientific and computing purposes
4. Universal Standard
- Used by: aviation, maritime navigation, meteorology, computing
- Internet timestamps use UTC
- GPS satellites broadcast UTC time
Historical Background: From GMT to UTC
The evolution of global time standards:
Before 1884: Local Solar Time
- Every city kept its own time based on sun position
- New York's noon was different from Philadelphia's noon
- Chaos for railways and telegraphs
1884: Greenwich Mean Time (GMT)
- International Meridian Conference establishes GMT
- Greenwich, London becomes global time reference
- Based on mean solar time at Royal Observatory
1960s: Atomic Precision
- Atomic clocks prove more accurate than Earth's rotation
- Earth's rotation is slowing (variable speed)
- Need for more precise standard
1967: UTC Born
- Coordinated Universal Time officially adopted
- Combines atomic time precision with Earth's rotation
- Leap seconds added to keep UTC aligned with solar time
1972: UTC Becomes Official
- Replaces GMT as international standard
- Computer systems worldwide adopt UTC
- Aviation and maritime industries mandate UTC
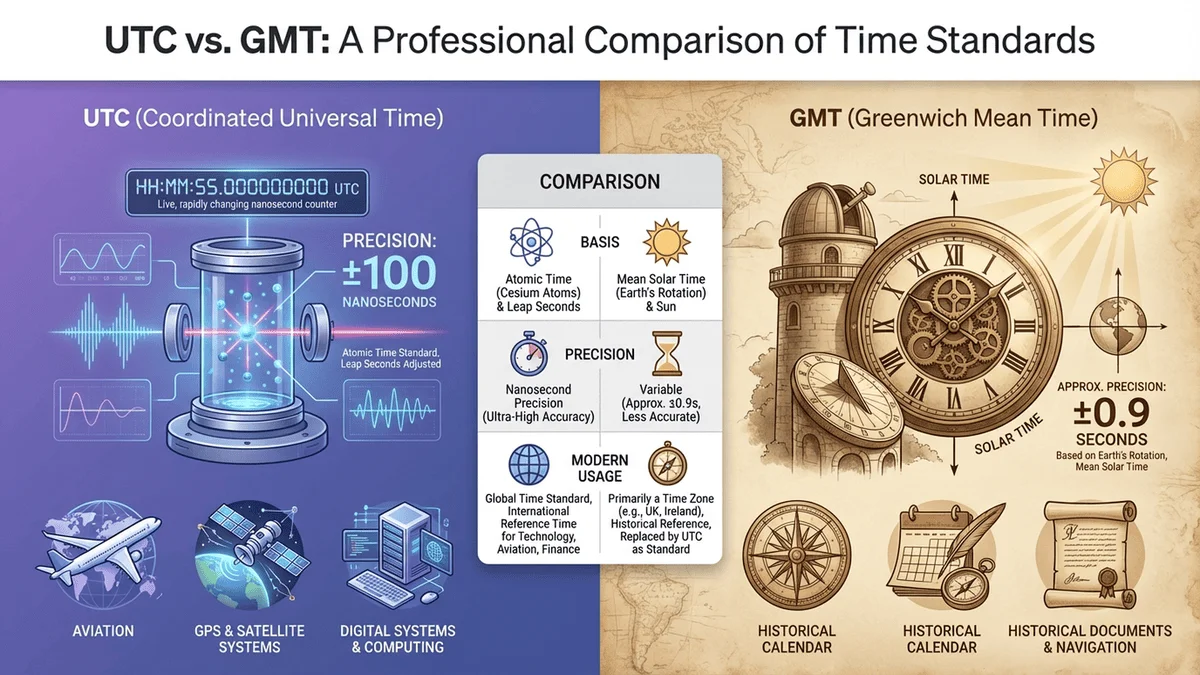
UTC vs GMT: What's the Difference?
For practical purposes, UTC and GMT are identical. They show the same time at the same moment.
Technical differences:
| Aspect | GMT | UTC |
|---|---|---|
| Basis | Mean solar time | Atomic time |
| Precision | ±0.9 seconds | Nanosecond precision |
| Official Use | Historical term | Modern standard |
| Leap Seconds | Not defined | Yes (to match Earth rotation) |
| Scientific Status | Obsolete for science | Current standard |
| Common Use | Still used colloquially | Preferred in technical contexts |
When to use which:
Use UTC:
- ✅ Software development and timestamps
- ✅ Scientific publications
- ✅ International aviation
- ✅ Official documentation
Use GMT:
- ✅ Casual conversation (UK)
- ✅ Historical references
- ✅ When communicating with general public
Reality check: Most digital systems labeled "GMT" actually use UTC. The terms are used interchangeably in everyday contexts.
How UTC Time Zone Works
The Offset System Explained
Every time zone on Earth is defined by its offset from UTC.
Offset format:
UTC±[hours]:[minutes]
Examples:
- UTC+0: Greenwich, London
- UTC-5: New York (EST)
- UTC+9: Tokyo
- UTC+5:30: Mumbai (half-hour offset)
- UTC+5:45: Nepal (45-minute offset)
How offsets work:
Positive offsets (UTC+X):
- East of Greenwich
- Ahead of UTC time
- Example: When it's 12:00 UTC, it's 21:00 in Tokyo (UTC+9)
Negative offsets (UTC-X):
- West of Greenwich
- Behind UTC time
- Example: When it's 12:00 UTC, it's 07:00 in New York (UTC-5)
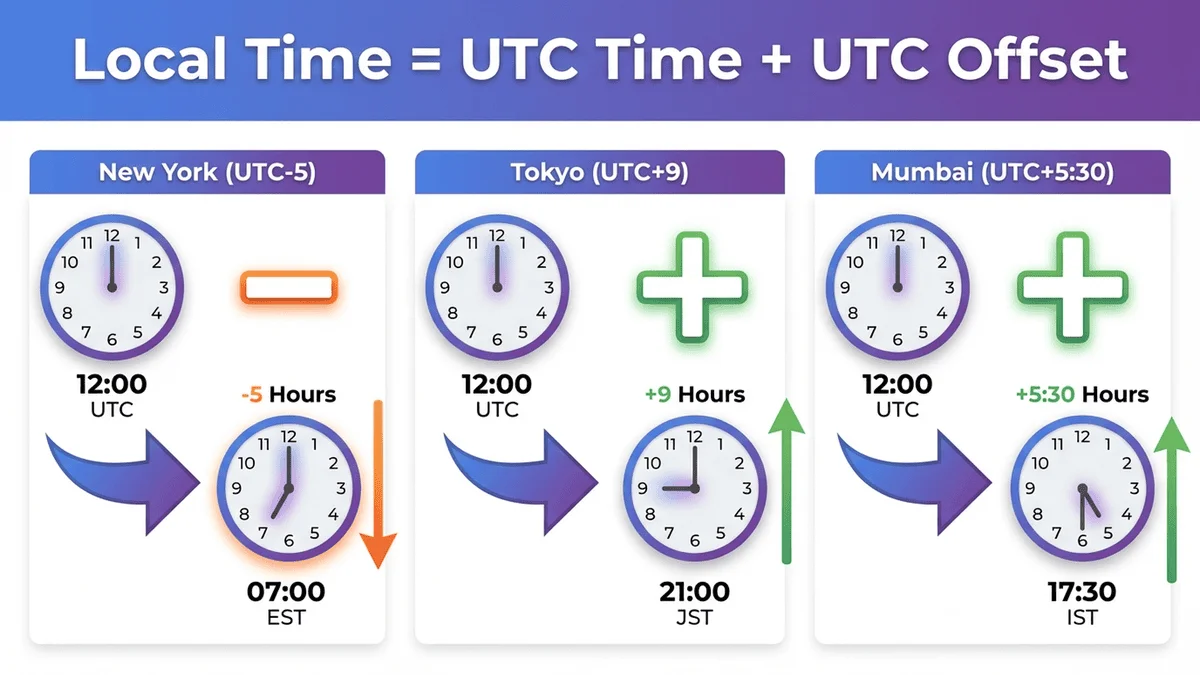
Calculation rule:
Local Time = UTC Time + UTC Offset
Example 1:
- UTC Time: 14:00 (2:00 PM)
- Location: Sydney (UTC+10)
- Calculation: 14:00 + 10 = 24:00 = 00:00 (midnight) next day
- Sydney Local Time: 12:00 AM (midnight)
Example 2:
- UTC Time: 09:00 (9:00 AM)
- Location: Los Angeles (UTC-8)
- Calculation: 09:00 + (-8) = 01:00
- LA Local Time: 1:00 AM
UTC Notation Standards
ISO 8601 Format (International Standard):
Format:
YYYY-MM-DDTHH:MM:SSZ
Example:
2025-01-27T14:30:00Z
Breakdown:
- 2025-01-27: Date (Year-Month-Day)
- T: Separator between date and time
- 14:30:00: Time (Hour:Minute:Second in 24-hour format)
- Z: "Zulu time" indicator (means UTC)
Why "Z" for UTC?
Military and aviation use "Z" to represent UTC. It comes from the NATO phonetic alphabet where "Z" = "Zulu." Time zones are assigned letters A-Z (except J), with Z reserved for UTC+0.
Common notation variations:
1. Explicit UTC:
2025-01-27 14:30:00 UTC
14:30 UTC
2:30 PM UTC
2. With milliseconds (computing):
2025-01-27T14:30:00.000Z
3. Unix timestamp (seconds since Jan 1, 1970 00:00:00 UTC):
1737989400
4. With offset notation:
2025-01-27T09:30:00-05:00 (EST)
2025-01-27T23:30:00+09:00 (JST)
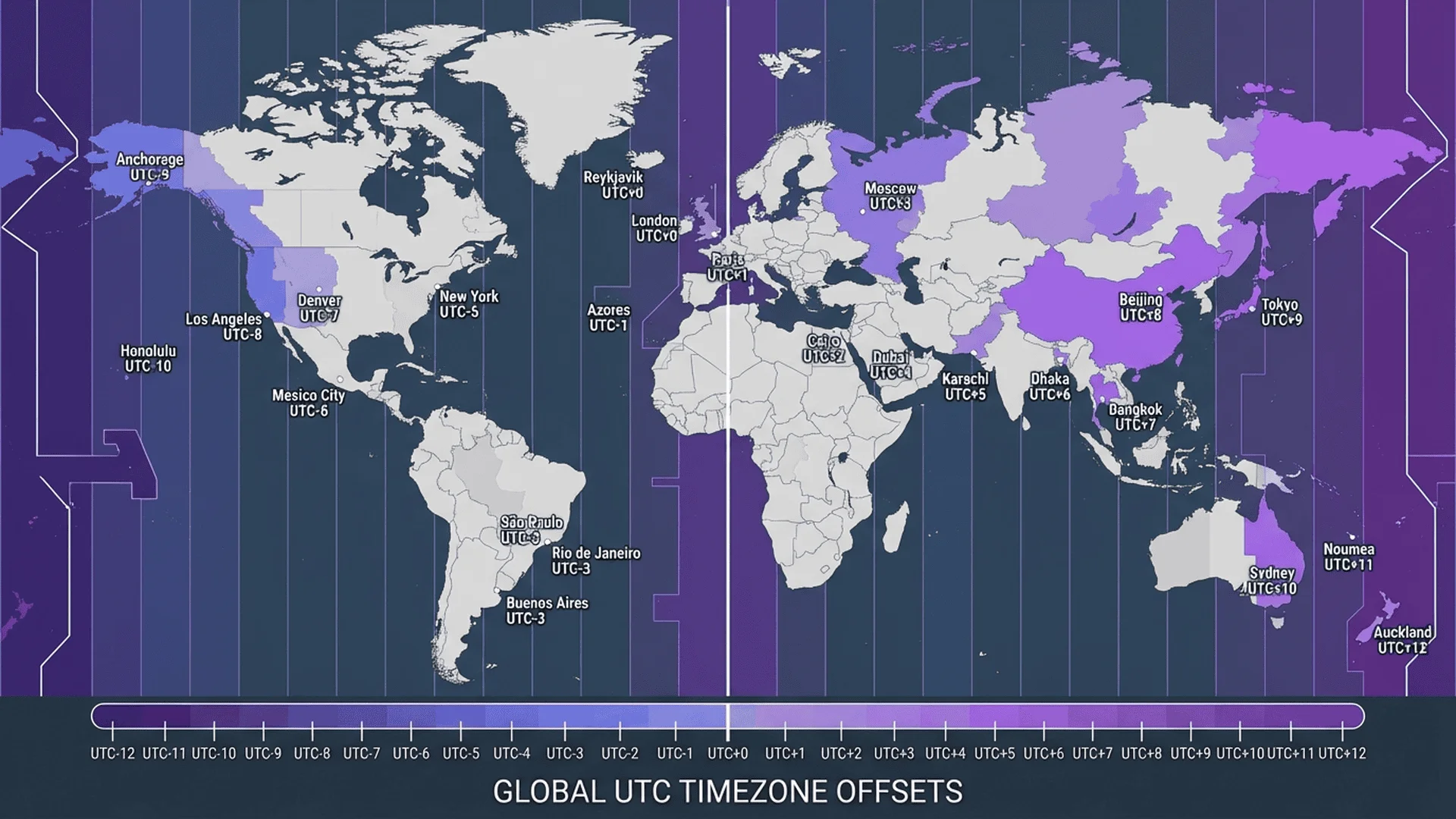
UTC Offset Around the World
Major Time Zones by UTC Offset
Complete reference table of major time zones:
| UTC Offset | Time Zone Name | Major Cities | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| UTC-12 | Baker Island Time | Baker Island (uninhabited) | Last time zone of the day |
| UTC-11 | SST (Samoa Standard Time) | Pago Pago | American Samoa |
| UTC-10 | HST (Hawaii Standard Time) | Honolulu | No DST |
| UTC-9 | AKST (Alaska Standard Time) | Anchorage | DST: UTC-8 |
| UTC-8 | PST (Pacific Standard Time) | Los Angeles, Seattle, Vancouver | DST: UTC-7 (PDT) |
| UTC-7 | MST (Mountain Standard Time) | Denver, Phoenix | Arizona: no DST |
| UTC-6 | CST (Central Standard Time) | Chicago, Mexico City | DST: UTC-5 (CDT) |
| UTC-5 | EST (Eastern Standard Time) | New York, Toronto, Miami | DST: UTC-4 (EDT) |
| UTC-4 | AST (Atlantic Standard Time) | Halifax, Puerto Rico, Caracas | Some areas use DST |
| UTC-3 | BRT (Brasília Time) | São Paulo, Buenos Aires | Some regions vary |
| UTC-2 | FNT (Fernando de Noronha Time) | Fernando de Noronha | Rarely used |
| UTC-1 | CVT (Cape Verde Time) | Praia | No DST |
| UTC+0 | UTC/GMT | London, Lisbon, Reykjavik | Greenwich reference |
| UTC+1 | CET (Central European Time) | Paris, Berlin, Rome | DST: UTC+2 (CEST) |
| UTC+2 | EET (Eastern European Time) | Athens, Cairo, Johannesburg | Some areas use DST |
| UTC+3 | MSK (Moscow Time) | Moscow, Istanbul, Nairobi | Russia: no DST |
| UTC+4 | GST (Gulf Standard Time) | Dubai, Abu Dhabi | No DST |
| UTC+5 | PKT (Pakistan Standard Time) | Karachi, Tashkent | No DST |
| UTC+5:30 | IST (Indian Standard Time) | Mumbai, Delhi, Bangalore | Half-hour offset, no DST |
| UTC+6 | BST (Bangladesh Standard Time) | Dhaka, Almaty | No DST |
| UTC+7 | ICT (Indochina Time) | Bangkok, Jakarta, Hanoi | No DST |
| UTC+8 | CST (China Standard Time) | Beijing, Singapore, Hong Kong | No DST |
| UTC+9 | JST (Japan Standard Time) | Tokyo, Seoul | No DST |
| UTC+9:30 | ACST (Australian Central) | Adelaide | Half-hour offset, DST: UTC+10:30 |
| UTC+10 | AEST (Australian Eastern) | Sydney, Melbourne | DST: UTC+11 (AEDT) |
| UTC+11 | SBT (Solomon Islands Time) | Honiara | No DST |
| UTC+12 | NZST (New Zealand Standard) | Auckland, Fiji | DST: UTC+13 (NZDT) |
Special cases to note:
Half-hour offsets:
- UTC+5:30 (India, Sri Lanka)
- UTC+9:30 (Australia Central)
- UTC+4:30 (Afghanistan)
- UTC-3:30 (Newfoundland, Canada)
45-minute offset:
- UTC+5:45 (Nepal - only 45-minute offset in the world)
Regions without DST:
- China (entire country uses UTC+8)
- Japan
- India
- Most of Africa
- Most of Middle East
💻 Instant UTC Conversion: Use our Time Zone Converter to convert UTC to any local time instantly. Select "UTC" as the source and your city as the destination—get accurate results including DST adjustments.

UTC to Local Time Conversion
Step-by-Step Conversion Method
Method 1: Simple Addition/Subtraction
Formula:
Local Time = UTC Time + UTC Offset
Example 1: UTC to Tokyo (UTC+9)
Given: 14:00 UTC (2:00 PM UTC)
Step 1: Identify Tokyo's offset: UTC+9
Step 2: Add offset: 14:00 + 9 hours = 23:00
Step 3: Result: 23:00 JST (11:00 PM Tokyo time)
Example 2: UTC to New York (UTC-5)
Given: 18:00 UTC (6:00 PM UTC)
Step 1: Identify New York's offset: UTC-5 (EST)
Step 2: Add offset: 18:00 + (-5) = 18:00 - 5 = 13:00
Step 3: Result: 13:00 EST (1:00 PM New York time)
Example 3: UTC to Mumbai (UTC+5:30)
Given: 08:00 UTC (8:00 AM UTC)
Step 1: Identify Mumbai's offset: UTC+5:30
Step 2: Add offset: 08:00 + 5 hours 30 minutes = 13:30
Step 3: Result: 13:30 IST (1:30 PM Mumbai time)
Handling Date Changes
Critical rule: When conversion crosses midnight (00:00), adjust the date.
Example 1: Date moves forward
Given: 22:00 UTC on January 27
Convert to: Tokyo (UTC+9)
Calculation: 22:00 + 9 = 31:00 = 07:00 next day
Result: 07:00 JST on January 28
Example 2: Date moves backward
Given: 03:00 UTC on January 28
Convert to: Los Angeles (UTC-8)
Calculation: 03:00 + (-8) = -05:00 = 19:00 previous day
Result: 19:00 PST on January 27
Quick reference for date changes:
When converting UTC to UTC+X (positive offset):
- If UTC time + offset ≥ 24:00 → Next day
- Subtract 24 from result and add 1 to date
When converting UTC to UTC-X (negative offset):
- If UTC time + offset < 00:00 → Previous day
- Add 24 to result and subtract 1 from date
Using Conversion Tools vs Manual Calculation
When to calculate manually:
- ✅ Learning purposes
- ✅ Simple, common conversions (UTC to EST, PST, etc.)
- ✅ When no internet/tools available
- ✅ Verifying automated results
When to use tools:
- ✅ Unfamiliar time zones
- ✅ Half-hour or 45-minute offsets
- ✅ Future dates (DST considerations)
- ✅ Multiple conversions needed
- ✅ Professional accuracy required
💻 Recommended Tool: Our Time Zone Converter handles all edge cases automatically:
- Automatic date adjustment
- DST detection for future dates
- Half-hour and 45-minute offsets
- Clear indication when date changes
- 100% free, no registration
Common UTC Conversion Examples
UTC to EST/EDT (New York)
Standard Time (EST): UTC-5
- Used: Early November to mid-March
- Calculation: UTC - 5 hours
Daylight Time (EDT): UTC-4
- Used: Mid-March to early November
- Calculation: UTC - 4 hours
Conversion examples:
| UTC Time | EST (Winter) | EDT (Summer) |
|---|---|---|
| 00:00 (midnight) | 7:00 PM previous day | 8:00 PM previous day |
| 06:00 (6 AM) | 1:00 AM | 2:00 AM |
| 12:00 (noon) | 7:00 AM | 8:00 AM |
| 18:00 (6 PM) | 1:00 PM | 2:00 PM |
| 23:00 (11 PM) | 6:00 PM | 7:00 PM |
Business hours overlay:
- New York business hours: 9:00 AM - 5:00 PM EST
- In UTC: 14:00 - 22:00 UTC (winter) or 13:00 - 21:00 UTC (summer)
Coordinating global teams? Using UTC as your reference point eliminates confusion. Our Meeting Planner Time Zone Guide shows you how to schedule across multiple time zones using UTC as the foundation.
UTC to PST/PDT (Los Angeles)
Standard Time (PST): UTC-8
- Used: Early November to mid-March
- Calculation: UTC - 8 hours
Daylight Time (PDT): UTC-7
- Used: Mid-March to early November
- Calculation: UTC - 7 hours
Conversion examples:
| UTC Time | PST (Winter) | PDT (Summer) |
|---|---|---|
| 00:00 (midnight) | 4:00 PM previous day | 5:00 PM previous day |
| 08:00 (8 AM) | 12:00 AM (midnight) | 1:00 AM |
| 16:00 (4 PM) | 8:00 AM | 9:00 AM |
| 20:00 (8 PM) | 12:00 PM (noon) | 1:00 PM |
| 23:59 | 3:59 PM | 4:59 PM |
Silicon Valley work hours:
- SF/LA business hours: 9:00 AM - 6:00 PM PST
- In UTC: 17:00 - 02:00 UTC next day (winter) or 16:00 - 01:00 UTC (summer)
UTC to IST (India)
Indian Standard Time: UTC+5:30 (year-round)
- No Daylight Saving Time
- Half-hour offset (unique)
- Calculation: UTC + 5 hours 30 minutes
Conversion examples:
| UTC Time | IST |
|---|---|
| 00:00 (midnight) | 5:30 AM |
| 04:00 (4 AM) | 9:30 AM |
| 08:00 (8 AM) | 1:30 PM |
| 12:00 (noon) | 5:30 PM |
| 18:00 (6 PM) | 11:30 PM |
| 20:00 (8 PM) | 1:30 AM next day |
India business hours:
- Typical working hours: 9:30 AM - 6:30 PM IST
- In UTC: 04:00 - 13:00 UTC
Why half-hour offset?
India chose UTC+5:30 to position the sun roughly overhead at noon in the center of the country. Using a full-hour offset would mean noon occurring significantly before or after solar noon.
Want detailed India-US time coordination strategies? Read our IST Time Zone Conversion Guide for:
- Best meeting times for India-US teams
- Working hour overlaps
- IST to EST/PST quick reference
- Cultural considerations for scheduling
UTC to JST (Tokyo)
Japan Standard Time: UTC+9 (year-round)
- No Daylight Saving Time
- Calculation: UTC + 9 hours
Conversion examples:
| UTC Time | JST |
|---|---|
| 00:00 (midnight) | 9:00 AM |
| 06:00 (6 AM) | 3:00 PM |
| 12:00 (noon) | 9:00 PM |
| 15:00 (3 PM) | 12:00 AM (midnight) next day |
| 18:00 (6 PM) | 3:00 AM next day |
| 23:00 (11 PM) | 8:00 AM next day |
Japan business hours:
- Typical working hours: 9:00 AM - 6:00 PM JST
- In UTC: 00:00 - 09:00 UTC
Tokyo Stock Exchange:
- Trading hours: 9:00 AM - 3:00 PM JST
- In UTC: 00:00 - 06:00 UTC
Trading forex or stocks globally? UTC is essential for tracking market sessions worldwide. Our Forex Trading Time Zone Guide explains how to use UTC to identify optimal trading windows, market overlaps, and session timing.
UTC to CET/CEST (Europe)
Central European Time (CET): UTC+1
- Used: Late October to late March
- Countries: Germany, France, Italy, Spain, Poland
Central European Summer Time (CEST): UTC+2
- Used: Late March to late October
- DST adds 1 hour
Conversion examples:
| UTC Time | CET (Winter) | CEST (Summer) |
|---|---|---|
| 00:00 (midnight) | 1:00 AM | 2:00 AM |
| 08:00 (8 AM) | 9:00 AM | 10:00 AM |
| 12:00 (noon) | 1:00 PM | 2:00 PM |
| 18:00 (6 PM) | 7:00 PM | 8:00 PM |
| 22:00 (10 PM) | 11:00 PM | 12:00 AM (midnight) next day |
European business hours:
- Typical hours: 9:00 AM - 6:00 PM CET
- In UTC: 08:00 - 17:00 UTC (winter) or 07:00 - 16:00 UTC (summer)
UTC in Technology and Aviation
UTC in Computer Systems
Why programmers love UTC:
1. Consistency
- Never changes (no DST)
- Single reference point worldwide
- Eliminates timezone-related bugs
2. Simplicity
- Store everything in UTC
- Convert to local time only for display
- Avoid complex timezone logic
3. Precision
- Atomic time accuracy
- Standardized across all systems
- No ambiguity
Common UTC uses in programming:
Database timestamps:
-- PostgreSQL example
CREATE TABLE events (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
created_at TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE DEFAULT NOW()
);
-- Stores in UTC, displays in user's timezone
API responses:
{
"timestamp": "2025-01-27T14:30:00Z",
"event": "user_login",
"user_id": 12345
}
Log files:
[2025-01-27T14:30:00.123Z] INFO: User logged in
[2025-01-27T14:30:01.456Z] INFO: Dashboard loaded
Unix timestamps (seconds since epoch):
// JavaScript example
const now = Date.now(); // Milliseconds since Jan 1, 1970 00:00:00 UTC
// 1737989400000
Best practices for developers:
- Always store in UTC
- Database: TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE (UTC)
-
Never store local times without timezone info
-
Convert at the edge
- Backend: Always UTC
-
Frontend: Convert to user's local timezone for display
-
Use ISO 8601 format
- Standard:
2025-01-27T14:30:00Z -
Unambiguous and universally understood
-
Account for leap seconds
- UTC includes leap seconds
- Important for high-precision systems
🔬 For Developers: Implementing UTC conversion in your application? Check our Time Zone Converter Implementation Guide for:
- Complete UTC conversion algorithms
- JavaScript/Python code examples
- DST handling logic
- Edge case management
- Best practices for timezone storage
UTC in Aviation
Aviation mandates UTC (called "Zulu Time" in aviation).
Why aviation uses UTC:
1. Safety
- Eliminates timezone confusion
- Pilots and controllers speak same time language
- Critical for international flights crossing multiple zones
2. Standardization
- Flight plans filed in UTC
- Weather reports (METARs/TAFs) timestamped in UTC
- Air traffic control worldwide uses UTC
3. Simplicity
- Flight durations calculated in UTC
- Fuel planning based on UTC departure/arrival
- Crew duty time tracked in UTC
Aviation time notation:
4-digit format:
1430Z = 14:30 UTC (2:30 PM UTC)
0600Z = 06:00 UTC (6:00 AM UTC)
2359Z = 23:59 UTC (11:59 PM UTC)
Zulu time examples:
Flight departure announcement:
"Passengers, our departure time is 1630 Zulu"
(4:30 PM UTC, regardless of local time)
Pilot radio communication:
"Tower, Flight BA123, requesting takeoff at 0845 Zulu"
Flight schedule:
Flight: BA123
Departure: London Heathrow (LHR) - 0800Z
Arrival: New York JFK - 1100Z
Duration: 3 hours (in UTC terms, but actual flight time considering timezone change)
Why "Zulu"?
Military and NATO phonetic alphabet:
- A-Z assigned to timezone offsets
- Z = UTC+0 (the zero/null offset)
- Phonetically: Alpha, Bravo, Charlie... Zulu
UTC in Other Industries
Maritime Navigation:
- Ship logs recorded in UTC
- Satellite navigation (GPS) broadcasts UTC
- International distress signals use UTC timestamps
Meteorology:
- Weather observations synchronized to UTC
- Forecast models run on UTC schedule
- Satellite imagery timestamped in UTC
Finance:
- Stock market opening/closing times referenced to UTC
- Forex trading uses UTC for session times
- Transaction timestamps in UTC
Space Agencies:
- NASA, ESA, SpaceX all use UTC
- Mission elapsed time (MET) calculated from UTC reference
- Satellite operations coordinated in UTC
Broadcasting:
- Live event times communicated in UTC
- International news synchronized to UTC
- Satellite uplinks scheduled in UTC
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What does UTC stand for?
UTC stands for "Coordinated Universal Time."
The acronym is a compromise between English "CUT" and French "TUC" (Temps Universel Coordonné). International organizations chose the neutral "UTC" to avoid language preference.
Not "Universal Time Coordinated" (though many think so).
2. Is UTC the same as GMT?
For practical purposes, yes. They show the same time at any given moment.
Technical difference:
- GMT (Greenwich Mean Time): Based on mean solar time, historical term
- UTC (Coordinated Universal Time): Based on atomic clocks, modern standard
In practice:
- Digital systems use UTC
- GMT still used colloquially (especially in UK)
- Time difference: Zero (they're synchronized)
3. Why doesn't UTC change for Daylight Saving Time?
UTC is a constant reference point.
Reasons:
1. Scientific standard: Atomic time doesn't change
2. Global coordination: Single unchanging reference needed
3. Computing reliability: Servers, databases need constant baseline
Individual time zones change for DST (e.g., EST→EDT), but their offset from UTC changes accordingly:
- EST: UTC-5 (winter)
- EDT: UTC-4 (summer)
- UTC itself: Always UTC+0
This design allows DST to be a local decision without affecting the global reference system.
4. How do I convert my local time to UTC?
Formula:
UTC Time = Local Time - Local UTC Offset
Example 1: New York to UTC (winter)
- Local time: 3:00 PM EST
- EST offset: UTC-5
- Calculation: 3:00 PM - (-5) = 3:00 PM + 5 = 8:00 PM UTC
Example 2: Tokyo to UTC
- Local time: 6:00 PM JST
- JST offset: UTC+9
- Calculation: 6:00 PM - (+9) = 6:00 PM - 9 = 9:00 AM UTC
Quick method: Use our Time Zone Converter:
1. Select your city
2. Select "UTC" as target
3. Instant accurate conversion
5. What is the UTC offset for my location?
Major city offsets:
Americas:
- Los Angeles: UTC-8 (PST) / UTC-7 (PDT)
- Denver: UTC-7 (MST) / UTC-6 (MDT)
- Chicago: UTC-6 (CST) / UTC-5 (CDT)
- New York: UTC-5 (EST) / UTC-4 (EDT)
Europe:
- London: UTC+0 (GMT) / UTC+1 (BST)
- Paris, Berlin: UTC+1 (CET) / UTC+2 (CEST)
- Athens: UTC+2 (EET) / UTC+3 (EEST)
Asia:
- Dubai: UTC+4
- Mumbai: UTC+5:30
- Singapore: UTC+8
- Tokyo: UTC+9
Oceania:
- Sydney: UTC+10 (AEST) / UTC+11 (AEDT)
- Auckland: UTC+12 (NZST) / UTC+13 (NZDT)
Find your offset: Our Time Zone Converter includes 200+ cities with current UTC offsets automatically detected.
6. Why do some time zones have 30 or 45 minute offsets?
Not all time zones are on full-hour offsets.
30-minute offsets:
- India (UTC+5:30): Positions sun overhead at noon in center of country
- Iran (UTC+3:30): Geographic and political reasons
- Afghanistan (UTC+4:30): Similar reasoning
- Myanmar (UTC+6:30): Historical colonial legacy
45-minute offset:
- Nepal (UTC+5:45): Only 45-minute offset globally, based on Kathmandu's longitude
Why?
- Geographic positioning: Align solar noon with clock noon
- Political boundaries: Don't follow meridian lines exactly
- Historical reasons: Colonial decisions or national identity
These offsets are valid and handled by all modern time systems.
7. What are leap seconds and how do they affect UTC?
Leap seconds keep UTC aligned with Earth's rotation.
The problem:
- Earth's rotation is slowing down
- Atomic clocks (UTC basis) are constant
- Over time, UTC and solar time drift apart
The solution:
- Add 1 second to UTC occasionally
- Keeps UTC within 0.9 seconds of solar time (UT1)
- Inserted at end of June 30 or December 31
Recent leap seconds:
- Last leap second: December 31, 2016 (23:59:60 UTC)
- Total since 1972: 27 leap seconds added
- Future leap seconds: Decided 6 months in advance
Impact on you:
- Minimal: Most people never notice
- Computers: Some systems have issues (Google "smears" leap seconds)
- High-precision applications: Must account for them
8. How accurate is UTC time?
Extremely accurate—beyond human perception.
UTC accuracy:
- Based on 400+ atomic clocks worldwide
- Accuracy: ±100 nanoseconds (0.0000001 seconds)
- More accurate than Earth's rotation
Comparison:
- Quartz watch: ±15 seconds/month
- Mechanical watch: ±30 seconds/day
- Smartphone (NTP sync): ±50 milliseconds
- Atomic clock (UTC source): ±100 nanoseconds
For practical purposes: UTC is "perfectly" accurate. Any error is in your device's clock sync, not UTC itself.
9. Can I set my computer to show UTC time?
Yes, though not commonly done.
Windows:
1. Settings → Time & Language → Date & time
2. Turn off "Set time zone automatically"
3. Select "(UTC) Coordinated Universal Time"
macOS:
1. System Preferences → Date & Time
2. Click Time Zone tab
3. Search for "GMT" or drag map to Greenwich, London
Linux:
sudo timedatectl set-timezone UTC
Better approach:
- Keep local timezone for daily use
- Use tools/apps to display UTC alongside local time
- Add UTC clock to taskbar/menu bar (most OSes support multiple clocks)
10. Why do websites and APIs use UTC?
UTC is the universal standard for digital systems.
Advantages for developers:
1. Consistency
- Store all timestamps in UTC
- No DST complications
- Single source of truth
2. Simplicity
- Convert to local time only for display
- Database queries simplified
- No timezone bugs
3. Interoperability
- All systems speak UTC
- API responses universally understood
- International users handled easily
4. Avoiding DST bugs
- DST transitions cause duplicate/missing hours
- UTC has no such issues
- Reliable for scheduling and logging
Best practice:
- Backend: Always use UTC
- Frontend: Convert to user's local timezone for display
- Storage: UTC timestamps with ISO 8601 format
Related Resources
Learn More About Time Zones
← Back to Time Zone Converter Complete Guide - Comprehensive overview of time zone conversion with practical examples
Understanding US Time Zones - Detailed guide to EST, PST, CST, MST and how they relate to UTC
IST Time Zone Conversion Guide - India-US time coordination strategies, best meeting times, and IST to UTC conversion
Explore Time Zone Tools
Time Zone Converter - Convert UTC to any local time instantly, with automatic DST detection
World Clock - Display multiple time zones simultaneously, including UTC reference
Date Calculator - Calculate future dates accounting for time zones and DST changes
Conclusion: UTC as Your Universal Reference
Master UTC, master time zones. Every time zone on Earth is defined by its relationship to UTC. Understanding UTC offsets, conversion methods, and notation standards gives you the foundation for flawless international coordination.
Key takeaways:
✅ UTC is the universal reference - based on atomic clocks, never changes
✅ All time zones are UTC offsets - positive (east) or negative (west)
✅ Conversion is simple math - Local Time = UTC + Offset
✅ UTC eliminates DST confusion - constant reference for computing and aviation
✅ Use tools for reliability - avoid manual calculation errors
Whether you're scheduling international meetings, developing software, or coordinating global operations—UTC is your anchor.
Next steps:
- Bookmark our Time Zone Converter - Free, accurate UTC conversions
- Read the Complete Time Zone Guide - Full context and advanced strategies
- Explore US Time Zones guide if working with American teams
- Master IST conversions for India-US collaboration
💡 Tool Master provides 33 free online tools including time zone converters, calculators, and productivity tools. All tools feature 100% local processing (your data never leaves your browser), no registration required, and dual language support.
References
- International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM) - Official UTC standard maintenance
- IANA Time Zone Database - Standard timezone data used globally
- International Telecommunication Union (ITU) - Coordination of world time
- U.S. Naval Observatory - Atomic clock operations for UTC
- International Earth Rotation Service (IERS) - Leap second decisions
- ISO 8601 - International date and time format standards
Last Updated: January 27, 2025
Article Type: Educational Guide
Word Count: 2,437 words
Reading Time: 11 minutes
Related Topics: Time zones, GMT, local time conversion, atomic time, international standards
Home | All Tools | Time Zone Converter | Technical Documentation