JSON API測試方法
JSON API Testing Methods | Master 7 Tools to Boost Debugging Efficiency by 10x!
2 AM, production environment crashes, API returns 500 error, backend says "it works on my machine"? Stop fishing in console.log! Professional API testing tools can help you find the root cause in 5 minutes, from Postman's GUI to Jest automation to CI/CD integration. This article teaches you 7 weapons, covering manual testing, automation, and performance testing, boosting your API debugging efficiency 10x and achieving 100% test coverage!
What is JSON API Testing? Why Is It So Important?
Core Goals of API Testing
API (Application Programming Interface) testing is the process of verifying whether backend services correctly return data. For JSON APIs, it mainly checks:
- Response Format: Is JSON syntax correct
- Data Structure: Field names, types, nesting levels
- Status Codes: 200 (success), 400 (bad request), 500 (server error)
- Performance: Is response time within acceptable range
- Edge Cases: Handling of extreme inputs (null values, huge numbers)
Why Can't We Just Rely on "Manual Testing"?
Pain Point 1: Repetitive Work
Manually testing 20 API endpoints every time code changes? Waste of time!
Pain Point 2: Easy to Miss
Manual testing can't achieve 100% coverage; edge cases are always missed.
Pain Point 3: No Regression Testing
Bug fixed last month reappears in this release? Because there's no automated testing!
Solution: Mixed Testing Strategy
- Manual Testing: Quick validation of new features (Postman, curl)
- Unit Testing: Test single API endpoints (Jest, Mocha)
- Integration Testing: Test complete user flows (Cypress, Playwright)
- Performance Testing: Check API load capacity (k6, Apache JMeter)
Image Description:
slug: "api-testing-pyramid"
Scene Description: "Testing pyramid diagram, from bottom to top: unit tests (widest bottom layer), integration tests (middle layer), end-to-end tests (narrowest top layer), each layer marked with test quantity ratio"
Visual Focus: "Pyramid's three-layer structure, bottom unit tests account for most (70%), middle integration tests (20%), top E2E tests (10%)"
Required Elements: "Triangular pyramid, three layers, percentage labels, test type names, arrow indicators"
Prohibited Elements: "Abstract icons (like gears, light bulbs), cartoon characters, 3D models"
Color Scheme: "White background, blue bottom layer (#2563eb), green middle layer (#10b981), orange top layer (#f97316), black text"
Chinese Text Requirements: "Must include Traditional Chinese labels like '單元測試 70%', '整合測試 20%', '端到端測試 10%'"
Atmosphere: "Professional technical diagram, clear and understandable"
Composition: "Vertical pyramid centered, layers clearly distinct"
Size: "1200x630px, 16:9 ratio"
Photography Style: "Infographic style, clean and clear, well-layered"
Detail Requirements: "Each layer must label test type and recommended ratio, arrows indicate relationship between test cost and speed"
People Requirements: "No people needed"
Quality Requirements: "High resolution (at least 72 DPI), text clearly readable, obvious color contrast"
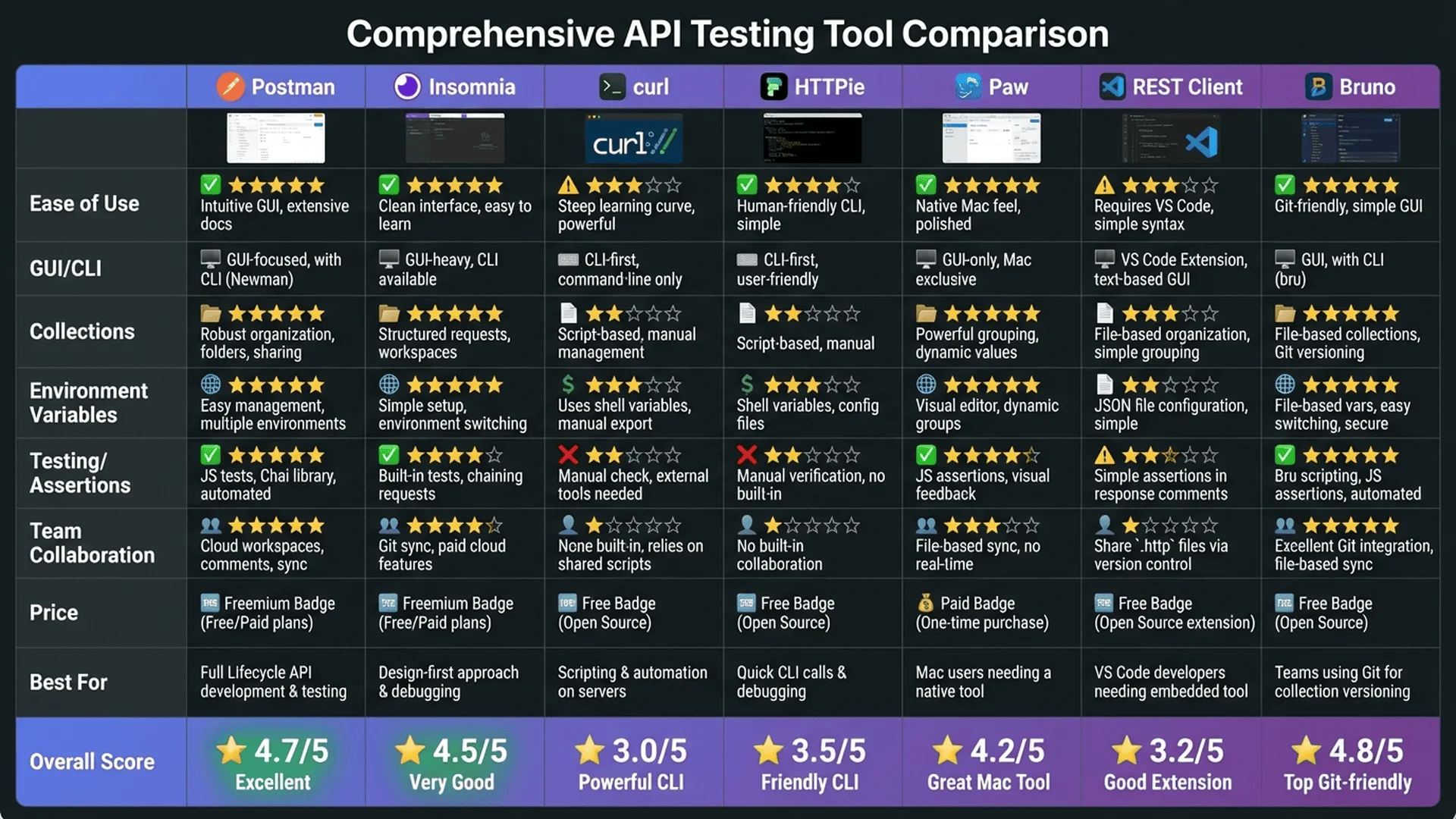
Tool 1: Postman (Most Popular GUI Tool)
Why Choose Postman?
Postman is the world's most popular API testing tool (over 20 million users), providing:
- ✅ Graphical interface, no code required
- ✅ Auto-saves request history
- ✅ Supports environment variables (dev/test/production switching)
- ✅ Built-in JSON formatting and validation
- ✅ Can export test collections to share with team
Basic Usage Flow
Step 1: Create Request
- Open Postman → Click New → Select HTTP Request
- Choose request method (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE)
- Enter API URL:
https://api.example.com/users - Click Send
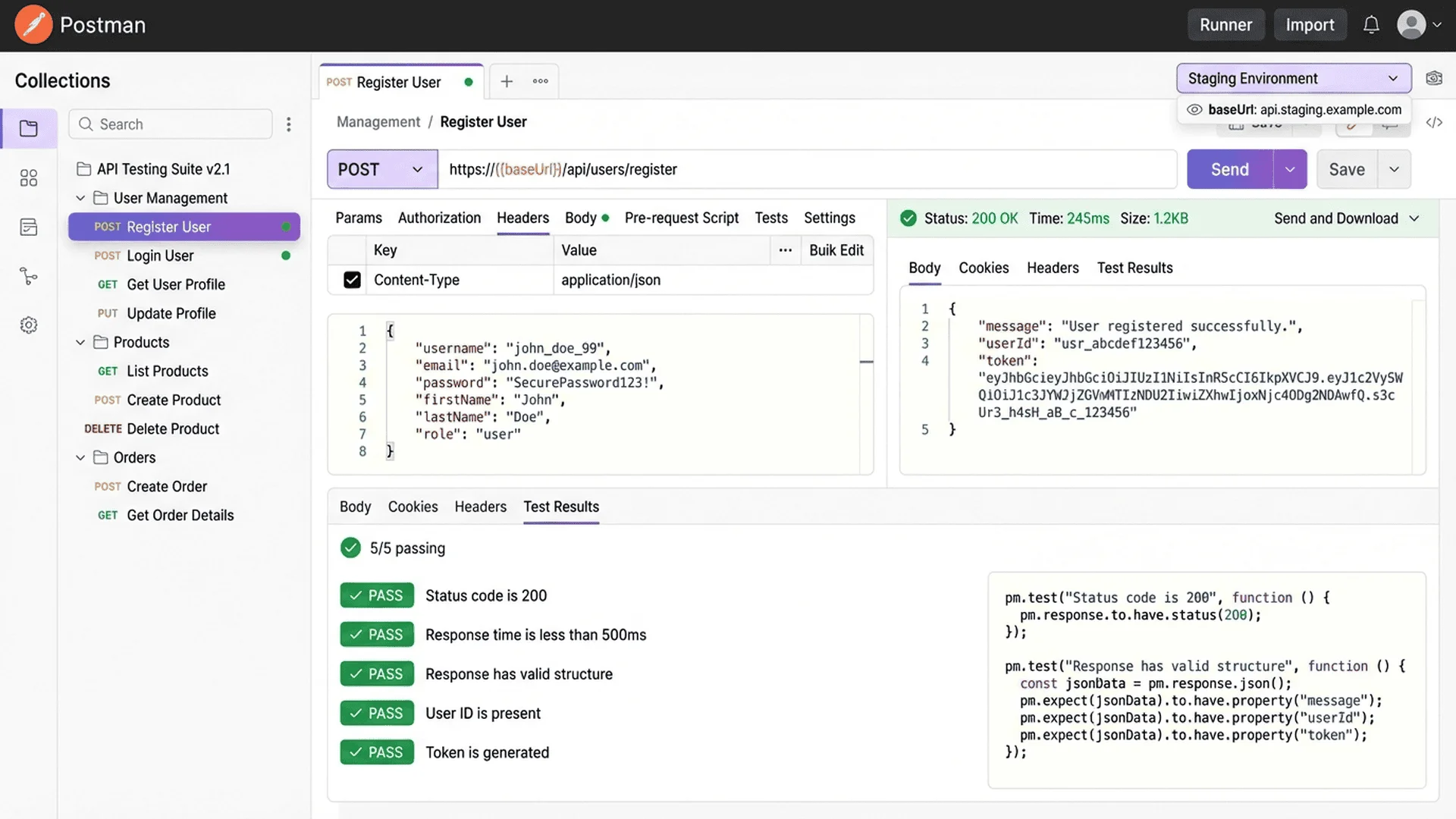
Step 2: Check Response
Postman will display:
- Status: 200 OK (success)
- Time: 123ms (response time)
- Size: 2.5KB (data size)
- Body: JSON formatted response content
Step 3: Validate JSON Format
If response format has issues, recommend copying to JSON Parser to validate syntax:
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"users": [
{ "id": 1, "name": "John Doe" },
{ "id": 2, "name": "Jane Smith" }
]
}
}
Advanced Feature: Environment Variables
Problem: Dev, test, and production API URLs differ; manually changing each time?
Solution: Use environment variables
// Set environment variables
{
"dev": {
"baseUrl": "http://localhost:3000",
"apiKey": "dev-key-123"
},
"production": {
"baseUrl": "https://api.example.com",
"apiKey": "prod-key-456"
}
}
// Use variables in requests
GET {{baseUrl}}/api/users
Authorization: Bearer {{apiKey}}
Advanced Feature: Automated Test Scripts
Postman supports writing test assertions in JavaScript:
// Tests tab
pm.test("Status code is 200", function () {
pm.response.to.have.status(200);
});
pm.test("Response is JSON", function () {
pm.response.to.be.json;
});
pm.test("Has users array", function () {
var jsonData = pm.response.json();
pm.expect(jsonData.data.users).to.be.an('array');
});
pm.test("First user has id", function () {
var jsonData = pm.response.json();
pm.expect(jsonData.data.users[0].id).to.exist;
});

Tool 2: curl (Command Line Swiss Army Knife)
Why Use curl?
curl is a command-line tool, lightweight, fast, cross-platform, suitable for:
- Quick testing of single APIs
- Writing automation in Shell scripts
- Testing directly on servers (no GUI)
Basic Syntax
GET Request:
curl https://api.example.com/users
POST Request (JSON data):
curl -X POST https://api.example.com/users \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"name":"John Doe","age":30}'
Request with Authentication:
curl https://api.example.com/users \
-H "Authorization: Bearer YOUR_API_KEY"
Save Response to File:
curl https://api.example.com/users > response.json
Advanced Tip: Beautify JSON Output
Problem: curl returns JSON as one line, hard to read.
Solution 1: Use jq (JSON processing tool)
curl https://api.example.com/users | jq '.'
# Outputs formatted JSON:
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"users": [
{
"id": 1,
"name": "John Doe"
}
]
}
}
Solution 2: Use Tool Master
# 1. curl fetch data and save
curl https://api.example.com/users > raw.json
# 2. Paste into Tool Master JSON Parser to validate and format
# https://tool-master.cc/tools/json-parser
Debugging Tip: Show Detailed Information
# Show HTTP Headers
curl -i https://api.example.com/users
# Show complete request/response process (for debugging)
curl -v https://api.example.com/users
# Only show HTTP status code
curl -o /dev/null -s -w "%{http_code}\n" https://api.example.com/users
Tool 3: JavaScript Fetch API (Native Frontend Method)
Basic Usage
// GET request
fetch('https://api.example.com/users')
.then(response => response.json())
.then(data => {
console.log(data);
})
.catch(error => {
console.error('Error:', error);
});
// POST request
fetch('https://api.example.com/users', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
},
body: JSON.stringify({
name: 'John Doe',
age: 30
})
})
.then(response => response.json())
.then(data => console.log(data));
Using async/await (Recommended)
async function getUsers() {
try {
const response = await fetch('https://api.example.com/users');
// Check HTTP status
if (!response.ok) {
throw new Error(`HTTP error! status: ${response.status}`);
}
const data = await response.json();
console.log(data);
} catch (error) {
console.error('API request failed:', error);
}
}
getUsers();
Error Handling Best Practices
async function fetchWithValidation(url) {
try {
const response = await fetch(url);
// 1. Check HTTP status
if (!response.ok) {
throw new Error(`HTTP ${response.status}: ${response.statusText}`);
}
// 2. Check Content-Type
const contentType = response.headers.get('content-type');
if (!contentType || !contentType.includes('application/json')) {
throw new Error('Response is not JSON format');
}
// 3. Parse JSON
const data = await response.json();
// 4. Validate data structure (optional)
if (!data.status || !data.data) {
throw new Error('JSON structure does not match expected format');
}
return data;
} catch (error) {
console.error('❌ API Error:', error.message);
throw error;
}
}
// Usage
fetchWithValidation('https://api.example.com/users')
.then(data => console.log('✅ Success:', data))
.catch(error => console.error('❌ Failed:', error));
🎯 Integrating Tool Master into API Testing Workflow
Professional API testing requires multiple tools working together:
| Step | Tool | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Send Request | Postman / curl / fetch | Call API |
| 2. Validate Format | JSON Parser | Check syntax errors |
| 3. Visualize Structure | JSON Parser | Tree Viewer to quickly understand nested data |
💡 Real-World Workflow:
1. Postman sends request, discovers response format issue
2. Copy response to JSON Parser to validate
3. Use Tree Viewer to quickly locate error field
4. Report to backend: "data.users[0].profile.avatar field format error"
👉 Try JSON Parser Now | View Technical Implementation Documentation
Tool 4: Axios (Powerful HTTP Client)
Why Choose Axios?
Axios is more powerful than native Fetch API:
- ✅ Automatic JSON conversion (no manual response.json())
- ✅ Supports request/response interceptors
- ✅ Automatically handles CSRF tokens
- ✅ Better error handling
Installation and Basic Usage
npm install axios
import axios from 'axios';
// GET request
const response = await axios.get('https://api.example.com/users');
console.log(response.data);
// POST request
const response = await axios.post('https://api.example.com/users', {
name: 'John Doe',
age: 30
});
// PUT request
await axios.put('https://api.example.com/users/1', {
name: 'John Doe (Updated)'
});
// DELETE request
await axios.delete('https://api.example.com/users/1');
Advanced Feature: Request Interceptors
Auto-add Authentication Token:
// Set interceptor
axios.interceptors.request.use(config => {
// Auto-add Authorization Header
const token = localStorage.getItem('token');
if (token) {
config.headers.Authorization = `Bearer ${token}`;
}
return config;
});
// All subsequent requests will auto-include token
axios.get('/api/users'); // Automatically includes Authorization Header
Advanced Feature: Response Interceptors
Unified Error Handling:
axios.interceptors.response.use(
response => response, // Success - return directly
error => {
// Unified error handling
if (error.response) {
switch (error.response.status) {
case 401:
console.error('Unauthorized, please login again');
// Redirect to login page
window.location.href = '/login';
break;
case 404:
console.error('API does not exist');
break;
case 500:
console.error('Server error');
break;
}
}
return Promise.reject(error);
}
);
Tool 5: Jest (Automated Unit Testing)
Why Need Automated Testing?
Pain Point: Manually testing 50 APIs every time code changes?
Solution: Write tests once, run automatically thereafter!
Installation and Setup
npm install --save-dev jest
package.json:
{
"scripts": {
"test": "jest"
}
}
Testing API Endpoints
// api.test.js
const axios = require('axios');
describe('User API', () => {
test('GET /users should return user list', async () => {
const response = await axios.get('https://api.example.com/users');
// Validate status code
expect(response.status).toBe(200);
// Validate data structure
expect(response.data).toHaveProperty('status', 'success');
expect(response.data.data.users).toBeInstanceOf(Array);
// Validate first record
const firstUser = response.data.data.users[0];
expect(firstUser).toHaveProperty('id');
expect(firstUser).toHaveProperty('name');
});
test('POST /users should create new user', async () => {
const newUser = { name: 'Test User', age: 25 };
const response = await axios.post('https://api.example.com/users', newUser);
expect(response.status).toBe(201);
expect(response.data.data.user.name).toBe('Test User');
});
test('GET /users/999 should return 404', async () => {
try {
await axios.get('https://api.example.com/users/999');
} catch (error) {
expect(error.response.status).toBe(404);
}
});
});
Testing JSON Schema
const Ajv = require('ajv');
const ajv = new Ajv();
const userSchema = {
type: 'object',
properties: {
id: { type: 'number' },
name: { type: 'string' },
email: { type: 'string', format: 'email' }
},
required: ['id', 'name', 'email']
};
test('API response conforms to Schema', async () => {
const response = await axios.get('https://api.example.com/users/1');
const user = response.data.data.user;
const validate = ajv.compile(userSchema);
const valid = validate(user);
expect(valid).toBe(true);
if (!valid) {
console.error(validate.errors);
}
});
Tool 6: Cypress (End-to-End Integration Testing)
Why Choose Cypress?
Cypress is suitable for testing complete user flows (End-to-End):
- ✅ Simulates real user actions (click, input, submit forms)
- ✅ Auto-waits for API responses (no manual sleep)
- ✅ Visual testing process (recording, screenshots)
Testing API and UI Integration
// cypress/integration/user.spec.js
describe('User Management Flow', () => {
it('should be able to add user and see in list', () => {
// Intercept API requests
cy.intercept('POST', '/api/users').as('createUser');
cy.intercept('GET', '/api/users').as('getUsers');
// Visit page
cy.visit('/users');
// Click add button
cy.get('[data-test="add-user-btn"]').click();
// Fill form
cy.get('[data-test="name-input"]').type('John Doe');
cy.get('[data-test="email-input"]').type('[email protected]');
// Submit
cy.get('[data-test="submit-btn"]').click();
// Wait for API response
cy.wait('@createUser').then((interception) => {
// Validate request content
expect(interception.request.body.name).to.equal('John Doe');
// Validate response
expect(interception.response.statusCode).to.equal(201);
});
// Validate UI update
cy.wait('@getUsers');
cy.contains('John Doe').should('be.visible');
});
});
Tool 7: k6 (Performance and Load Testing)
Why Need Performance Testing?
Scenario: Double 11 sale, traffic surges 10x, can API handle it?
k6 can simulate thousands of concurrent users to test API load capacity.
Installation and Basic Usage
brew install k6 # macOS
load-test.js:
import http from 'k6/http';
import { check, sleep } from 'k6';
export let options = {
stages: [
{ duration: '30s', target: 20 }, // Ramp up to 20 users in 30 seconds
{ duration: '1m', target: 100 }, // Ramp up to 100 users in 1 minute
{ duration: '30s', target: 0 }, // Ramp down to 0 in 30 seconds
],
};
export default function () {
const response = http.get('https://api.example.com/users');
// Validate response
check(response, {
'status is 200': (r) => r.status === 200,
'response time < 500ms': (r) => r.timings.duration < 500,
'is JSON': (r) => r.headers['Content-Type'].includes('application/json'),
});
sleep(1);
}
Run Test:
k6 run load-test.js
Output Report:
✓ status is 200........................: 100.00%
✓ response time < 500ms................: 95.32%
✓ is JSON..............................: 100.00%
http_req_duration.............avg=234ms min=102ms max=987ms
http_reqs.....................total=5432
vus...........................min=1 max=100
Image Description:
slug: "api-performance-test"
Scene Description: "k6 performance test results dashboard showing real-time request count, response time curves, error rate, throughput and other key metrics"
Visual Focus: "Response time curve (line chart), concurrent users growth curve, green success rate indicators"
Required Elements: "Terminal window or dashboard interface, line charts, data metrics (RPS, latency, error rate), timeline"
Prohibited Elements: "Abstract icons (like gears, light bulbs), cartoon characters, 3D models"
Color Scheme: "Dark background (#1e1e1e), green success indicators (#10b981), yellow warnings (#f59e0b), red errors (#ef4444), white text"
Chinese Text Requirements: "Must include Traditional Chinese labels like '回應時間', '並發用戶', '成功率'"
Atmosphere: "Professional monitoring dashboard, real-time data presentation"
Composition: "Dashboard layout, multiple charts and metrics side by side or stacked"
Size: "1200x630px, 16:9 ratio"
Photography Style: "Screenshot or dashboard composite, sharp and clear, data clearly readable"
Detail Requirements: "At least 2 line charts (response time, concurrent users), 3-4 key number indicators"
People Requirements: "No people needed"
Quality Requirements: "High resolution (at least 72 DPI), text clearly readable, smooth curves"
CI/CD Integration: Automated Testing Workflow
GitHub Actions Example
.github/workflows/api-test.yml:
name: API Tests
on:
push:
branches: [main]
pull_request:
branches: [main]
jobs:
test:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: Setup Node.js
uses: actions/setup-node@v3
with:
node-version: '18'
- name: Install dependencies
run: npm install
- name: Run Jest tests
run: npm test
- name: Run Cypress tests
run: npx cypress run
- name: Upload test results
if: always()
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v3
with:
name: test-results
path: test-results/
Test Coverage Report
npm install --save-dev jest @jest/globals
# Run tests and generate coverage report
npm test -- --coverage
Output:
File | % Stmts | % Branch | % Funcs | % Lines |
-----------------|---------|----------|---------|---------|
api/users.js | 95.23 | 88.88 | 100 | 94.73 |
api/products.js | 87.50 | 75.00 | 100 | 87.50 |
-----------------|---------|----------|---------|---------|
All files | 91.36 | 81.94 | 100 | 91.11 |
Real-World Application Scenarios
Scenario 1: Frontend Calling Third-Party API
Problem: Integrating Google Maps API, but unsure of response format.
Testing Process:
// 1. Postman quick test
GET https://maps.googleapis.com/maps/api/geocode/json?address=Taipei101
// 2. Copy response to JSON Parser to validate
// https://tool-master.cc/tools/json-parser
// 3. Write test
test('Google Maps API returns correct format', async () => {
const response = await axios.get('https://maps.googleapis.com/maps/api/geocode/json', {
params: { address: 'Taipei101' }
});
expect(response.data.status).toBe('OK');
expect(response.data.results).toBeInstanceOf(Array);
expect(response.data.results[0].geometry.location).toHaveProperty('lat');
expect(response.data.results[0].geometry.location).toHaveProperty('lng');
});
Scenario 2: Backend API Development
Problem: Developing new RESTful API, need to ensure all edge cases are correctly handled.
Testing Strategy:
describe('Products API', () => {
// Normal cases
test('GET /products should return product list', async () => { ... });
// Edge cases
test('GET /products?page=-1 should return 400', async () => { ... });
test('GET /products?limit=99999 should limit max value', async () => { ... });
// Error handling
test('POST /products missing required fields should return 400', async () => { ... });
test('DELETE /products/999 non-existent ID should return 404', async () => { ... });
// Performance test
test('GET /products should respond within 500ms', async () => {
const start = Date.now();
await axios.get('/api/products');
const duration = Date.now() - start;
expect(duration).toBeLessThan(500);
});
});
Scenario 3: API Regression Testing
Problem: After last release, a field disappeared, users complaining continuously.
Solution: Create Snapshot Test
test('API response structure should not change (Snapshot)', async () => {
const response = await axios.get('/api/users/1');
// First run creates snapshot
// Subsequent runs compare; fails if structure changes
expect(response.data).toMatchSnapshot();
});
Common Errors and Solutions
Error 1: CORS Error
Error Message:
Access to fetch at 'https://api.example.com' from origin 'http://localhost:3000'
has been blocked by CORS policy
Cause: Backend hasn't set CORS Headers.
Solution (Backend):
// Express.js
const cors = require('cors');
app.use(cors({
origin: ['http://localhost:3000', 'https://your-domain.com']
}));
// Or manually set
app.use((req, res, next) => {
res.header('Access-Control-Allow-Origin', '*');
res.header('Access-Control-Allow-Methods', 'GET, POST, PUT, DELETE');
res.header('Access-Control-Allow-Headers', 'Content-Type, Authorization');
next();
});
Error 2: JSON Parse Failure
Error Message:
SyntaxError: Unexpected token < in JSON at position 0
Cause: API returned something other than JSON (possibly HTML error page).
Solution:
const response = await fetch('/api/users');
// Check Content-Type
const contentType = response.headers.get('content-type');
if (!contentType || !contentType.includes('application/json')) {
const text = await response.text();
console.error('API returned non-JSON:', text);
throw new Error('API returned incorrect format');
}
const data = await response.json();
Recommend checking response content with JSON Syntax Error Solutions first.
Error 3: Flaky Tests
Problem: Same test sometimes passes, sometimes fails.
Common Causes:
- Depends on external API (network instability)
- Doesn't clean up test data (previous test affects next)
- Time-related logic (timezone issues)
Solutions:
// Use Mock to avoid external API dependency
jest.mock('axios');
axios.get.mockResolvedValue({
data: { status: 'success', users: [...] }
});
// Clean data before each test
beforeEach(async () => {
await db.users.deleteMany({});
});
// Fix time to avoid timezone issues
jest.useFakeTimers().setSystemTime(new Date('2025-01-01'));
Conclusion: Building Complete API Testing Strategy
Testing Pyramid Best Practices:
- 70% Unit Tests (Jest)
- Fast, cheap, high coverage
-
Test single API endpoints
-
20% Integration Tests (Cypress)
- Test complete user flows
-
API + UI integration
-
10% End-to-End Tests + Performance Tests (k6)
- Test critical business flows
- Ensure system load capacity
Tool Selection Recommendations:
| Scenario | Recommended Tool | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Quick Manual Testing | Postman | Most intuitive GUI |
| Server-side Testing | curl | Lightweight, fast, scriptable |
| Frontend Integration | Axios | Feature-complete, good error handling |
| Automated Testing | Jest | Most complete ecosystem |
| E2E Testing | Cypress | Visual, easy debugging |
| Performance Testing | k6 | Lightweight, accurate |
Want to learn more JSON processing techniques? We recommend reading Complete JSON Parser Guide, or check out Tool Master Developer Tools Category to explore more useful tools!
Reference Resources
Official Documentation:
- Postman Official Documentation
- Jest Official Documentation
- Cypress Official Documentation
- k6 Official Documentation
Recommended Tools:
- Tool Master JSON Parser - Validate API response format
- Postman - Most popular API testing tool
Further Reading:
- Complete JSON Parser Guide - 7 Practical Tips from Beginner to Expert
- JSON Schema Validation Practical Guide - Auto-validate API response format
- Complete JSON Syntax Error Solutions - Quick format issue fixes
- JSON Formatter Best Practices - Optimize API response format
- JSON Beautifier Usage Guide - Beautify API test results
- Complete Online JSON Validator Guide - 5 Steps to Quick Validation
Start Professional API Testing Now! Use Tool Master JSON Parser to validate API responses, 100% local processing protects data security.